- Tally Prime Installation
- Tally Prime – Accounts – Basic – Tamil
- Tally Prime இல் Ledger உருவாக்குவது எப்படி – Example 1
- Tally Prime இல் Ledger உருவாக்குவது எப்படி – Example 2
- Tally Accounting Software – Simple Voucher Entry
- Tally Prime இல் Accounting Vouchers – Part 1 | Tally Prime Tutorial in Tamil”
- Learn Tally Prime in Tamil | Inventory Management | How Create Stock Item, Groups,Category and Units
- Tally Prime Tutorial in Tamil | Inventory | How Create Stock Item, Group, Category, Location
Tag: Tally Prime
-
Learn Tally Prime – Tamil Tutorials Videos Links
-
Tally Prime – Step by Step to Create Ledgers – Example 1
- First Create a new company named Royal Trading & Co
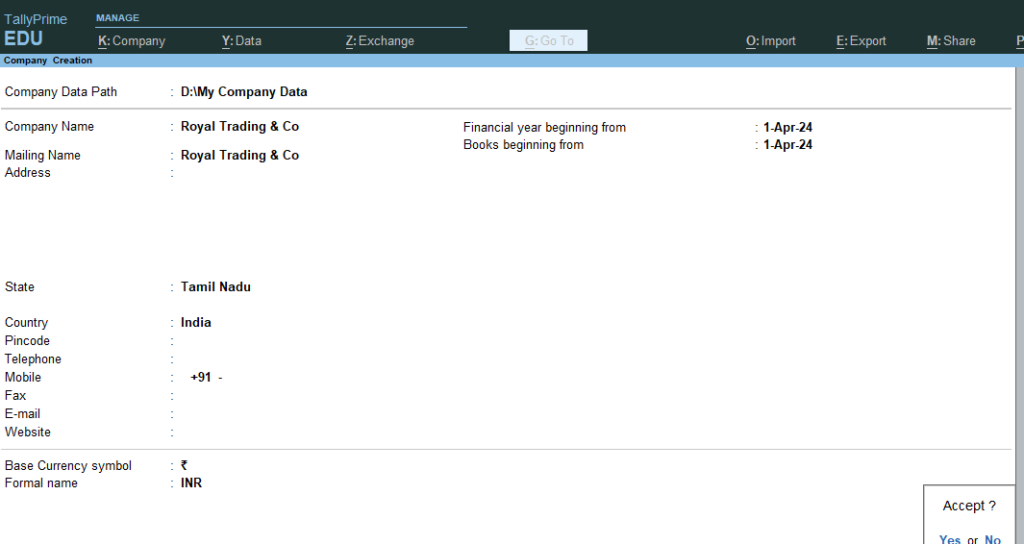
2. After Company Creation > First Create the following ledgers >
Ledger Name Group Debit (₹) Credit (₹) Ramu Capital Account Capital Account 10000 Cash in Hand Cash-in-Hand 10000 3. Gateway of Tally > Masters : Create > Ledgers:
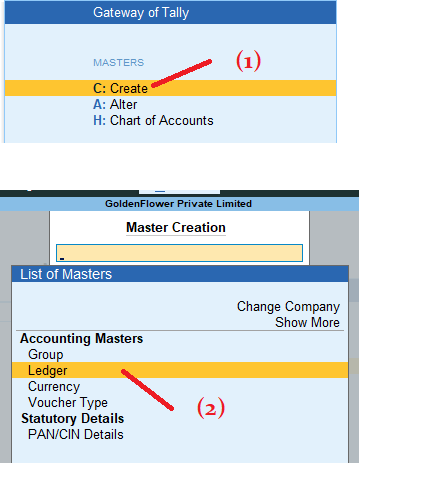
4. Enter Name : Ramu Capital A/c — Under : Type Cap and Select Right Side Using Arrow Keys or Select and Enter Capital Account > and Give Opening Balance : 10000 Cr. > Accept Yes >
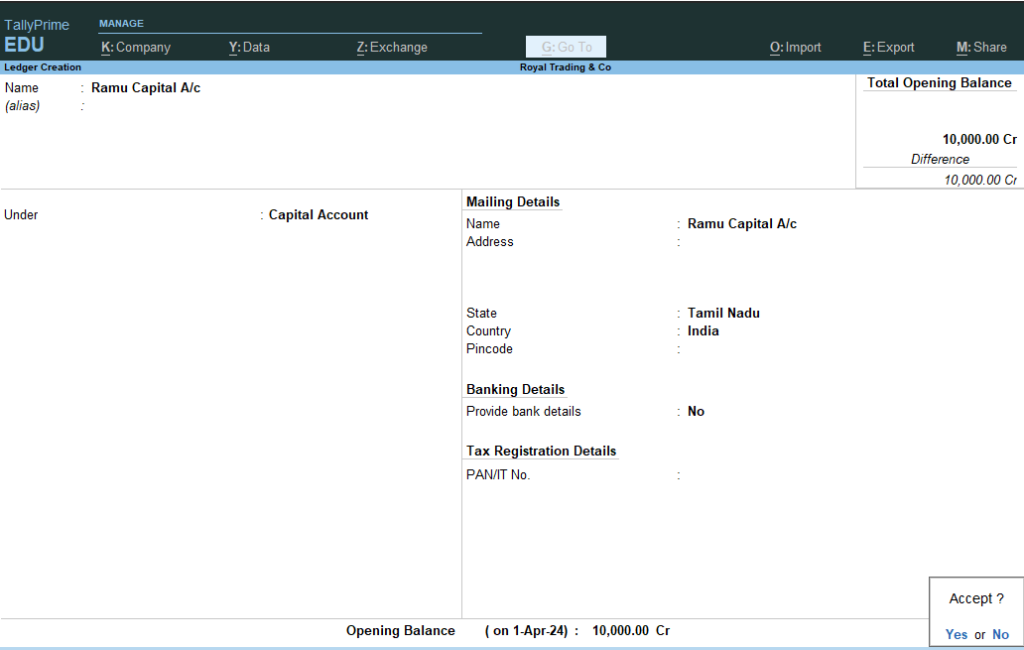
5. Now you will see the Same Ledger creation > Press Escape twice and Goto Gateway of Tally >
6. Gateway of Tally > Master : Alter > Ledgers > Select Cash > Opening Balance : 10000 Dr.
7. So Ramu is Giver and Cash is Comes in to Business . So Cr. Ramu Capital A/c and Dr. Cash A/c
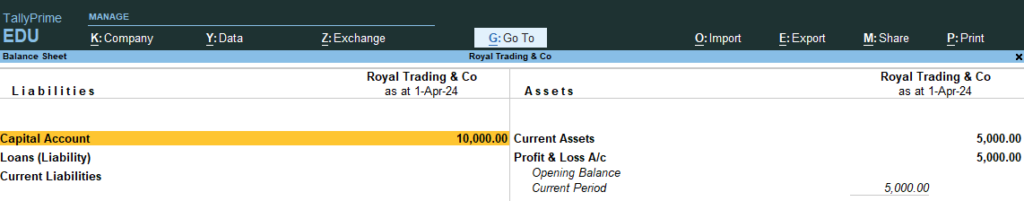
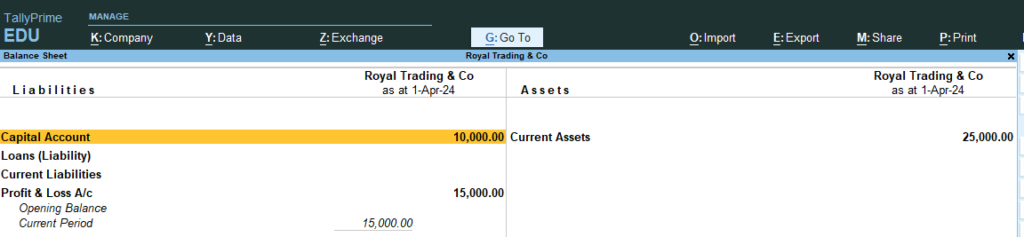
8. Go Gateway of Tally > Go Balance Sheet > You Can See Liabilities / Current Assets Statement
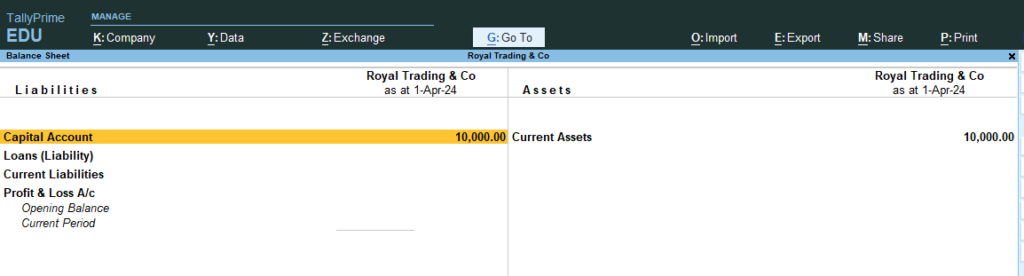
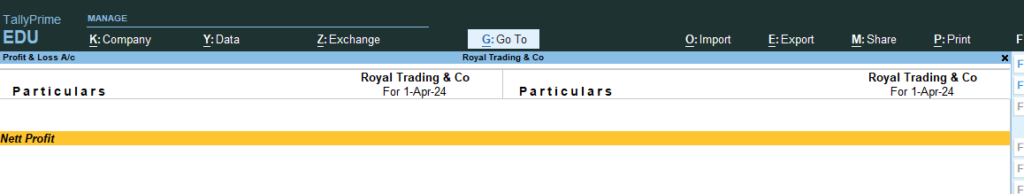
9. Go Gateway of Tally > Go Profit and Loss A/c > No Profit and Loss Data because no entry made in any purchase or sales
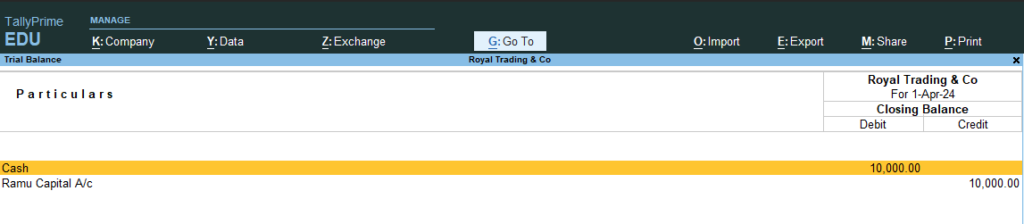
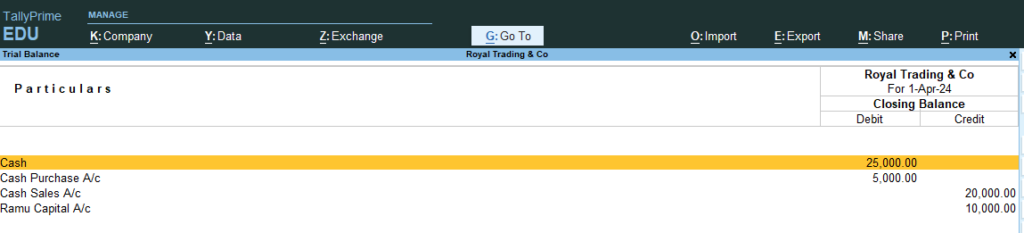
10. Go Gateway of Tally > Go Display More Reports or Press D > Go Trail Balance > and Press F5 (Ledger Wise / Group wise breakup)
11. Now Add the following Ledger
Ledger Name Group Debit (₹) Credit (₹) Cash Purchase A/c Purchase 5000 Go Gateway of Tally > Enter Name : Cash Purchase A/c — Under : Select Purchase Account > and Give Opening Balance : 5000 Cr. > Accept Yes >
Gateway of Tally > Master : Alter > Ledgers > Select Cash > Opening Balance : 5000 Dr. (Because Amount to be reduced due to Cash purchase Rs.5000)
12. Now Go the Step No 8 , 9, 10 (See the changes in Profit and Loss and Balance sheet , now net loss Because Only Cash Purchase Not Sales ..)
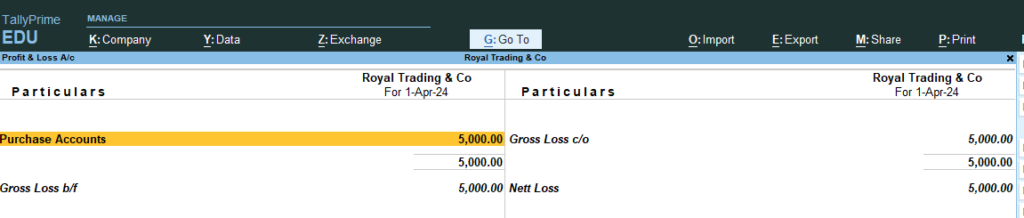
13. Now Add the following Ledger
Ledger Name Group Debit (₹) Credit (₹) Cash Sales A/c Sales 20000 Go Gateway of Tally > Master > Create : Ledgers > Enter Name : Cash Sales A/c — Under : Select Sales Account > and Give Opening Balance : 20000 Dr. > Accept Yes >
Gateway of Tally > Master : Alter > Ledgers > Select Cash > Opening Balance : 25000 Dr. (Because Amount to be raised due to Cash Sales Rs.20000)
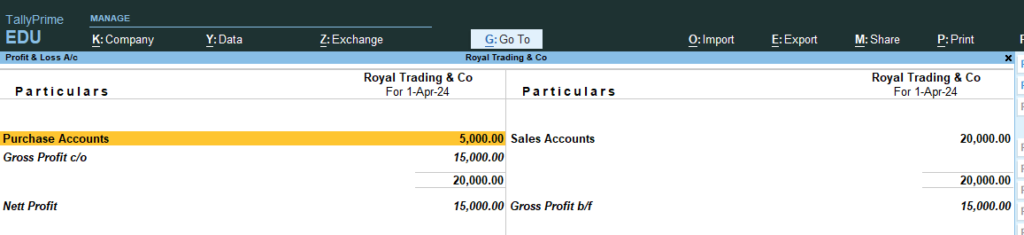
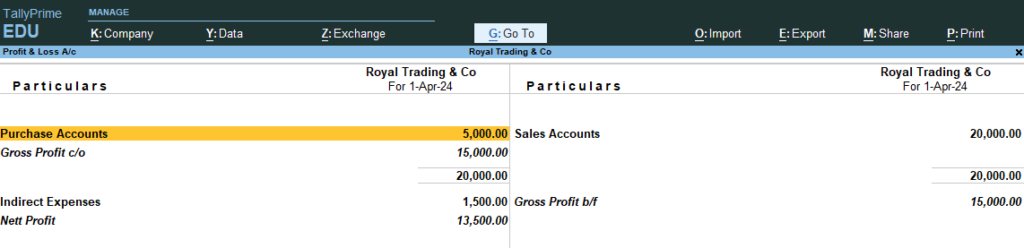
14. Now Go the Step No 8 , 9, 10 (See the changes in Profit and Loss and Balance sheet)
Profit and Loss A/c
Balance Sheet
Trail Balance
13. Now Add the following Ledger
Ledger Name Group Debit (₹) Credit (₹) Furniture Fixed Asset 5000 Telephone Charges Indirect Expenses 1000 Electricity Bill Paid Indirect Expenses 500 Total 6500 14. Go Gateway of Tally > Master > Create : Ledgers > Name : Furniture — Under : Fixed Asset > and Give Opening Balance : 5000 Dr. > Accept Yes >
15. Name : Telephone Charges — Under : Indirect Expenses > and Give Opening Balance : 1000 Dr.
16. Name : Electricity Bill Paid — Under : Indirect Expenses > and Give Opening Balance : 500 Dr.
17, Gateway of Tally > Master : Alter > Ledgers > Select Cash > Opening Balance : 18500 Dr. (Because Amount to be reduced due to Expenses (25000- 6500 = 18500 Dr.)
18. Now Go the Step No 8 , 9, 10 (See the changes in Profit and Loss and Balance sheet)
If any doubt say comments … thanks
Continue…..
-
Tally Prime – Step by Step to Create Ledgers – Example 2
This example covers how to create ledgers and how they affect the profit and loss statement and balance sheet.
Please follow the steps and share your feedback in the comments section once completed
Ledger Name Group Debit (₹) Credit (₹) Rama Capital Account Capital Account 5,00,000 Cash in Hand Cash-in-Hand 1,00,000 SBI A/c Bank Accounts 2,00,000 Sales Sales Account 3,00,000 Purchase Purchase Account 1,50,000 Sundry Debtor – A Sundry Debtors 50,000 Sundry Creditor – B Sundry Creditors 75,000 Office Equipment Fixed Assets 2,20,000 Salary Expenses Indirect Expenses 1,70,000 Rent Expenses Indirect Expenses 40,000 Outstanding Expenses Current Liabilities 30,000 Commission Received Indirect Incomes 25,000 Step 1:
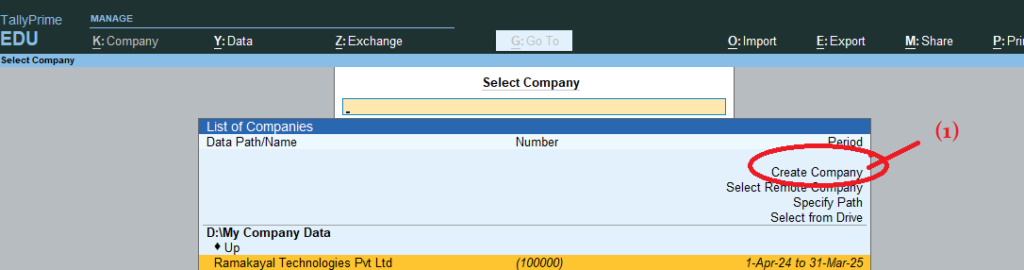
Create a Company:
- Open Tally Prime & Click Create Company
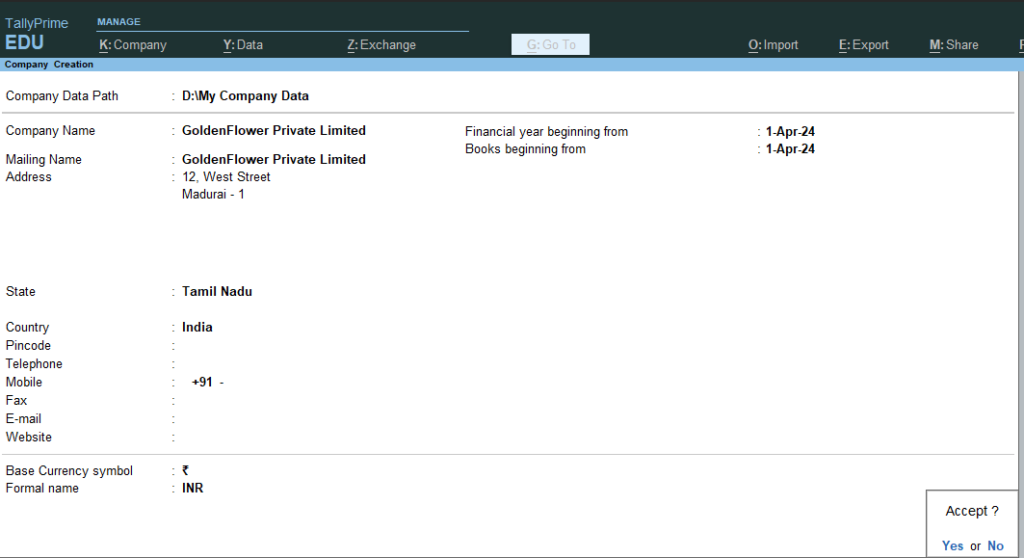
2. Fill in the necessary details like company name, address, etc.,
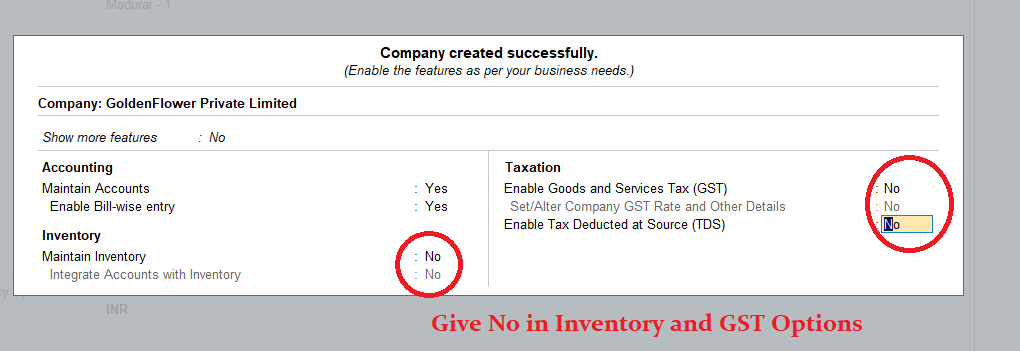
3) After accepting the company creation screen, you will see the Company Features window. Set the ‘Maintain Inventory’ option to ‘No’ and the ‘Enable Goods and Services Tax (GST)‘ option to ‘No.’ Ensure that these settings match the screen below

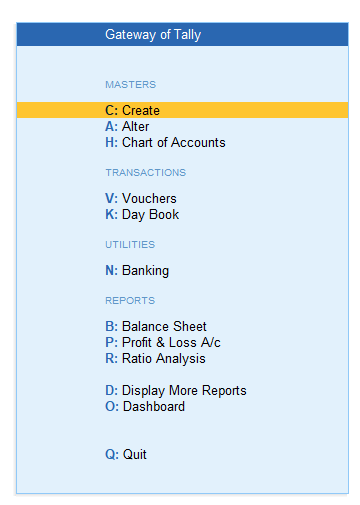
4) After accepting the company features screen (Note: To accept any screen, press CTRL + A), you will see the Gateway of Tally.
5) Now create a ledger name called Rama Capital account with opening balance : Rs. 5,00,000
Ledger Name Group Debit (₹) Credit (₹) Rama Capital Account Capital Account 5,00,000 
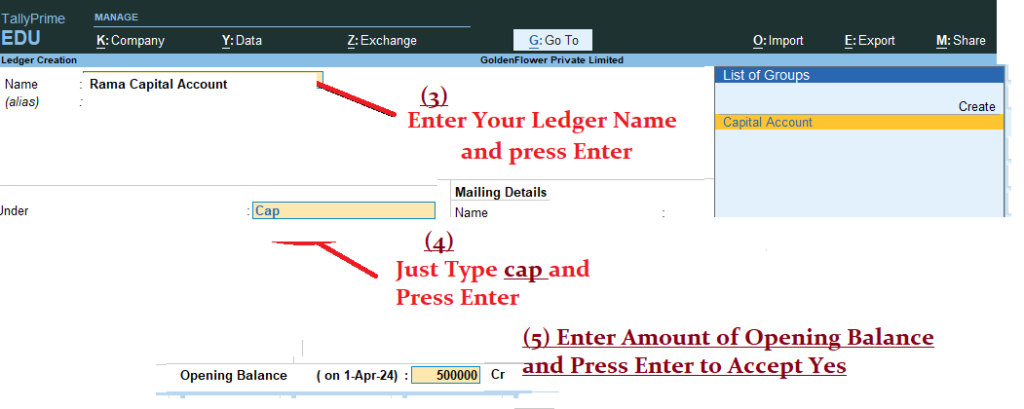
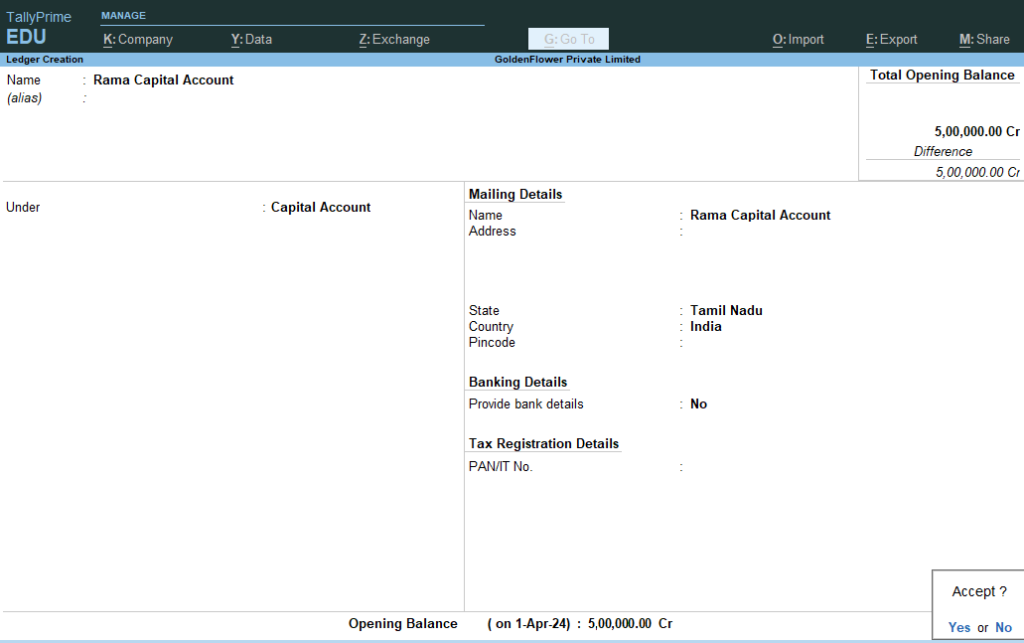
Gateway of Tally > Masters > Create > Ledger > Name : Rama Capital Account Under : Capital Account and Opening Balance 5,00,000 Cr> Accept Yes ( Now Press Escape key Twice to see Gateway of Tally)6) Next
Ledger Name Group Debit (₹) Credit (₹) Cash in Hand Cash-in-Hand 1,00,000 Go Gateway of Tally > Masters > Alter > Ledgers > Select : Cash > Press Enter to see the below screen > Now Go to the Opening Balance Field using Enter Key > Give Opening Balance : 1,00,000 Dr > Accept : Yes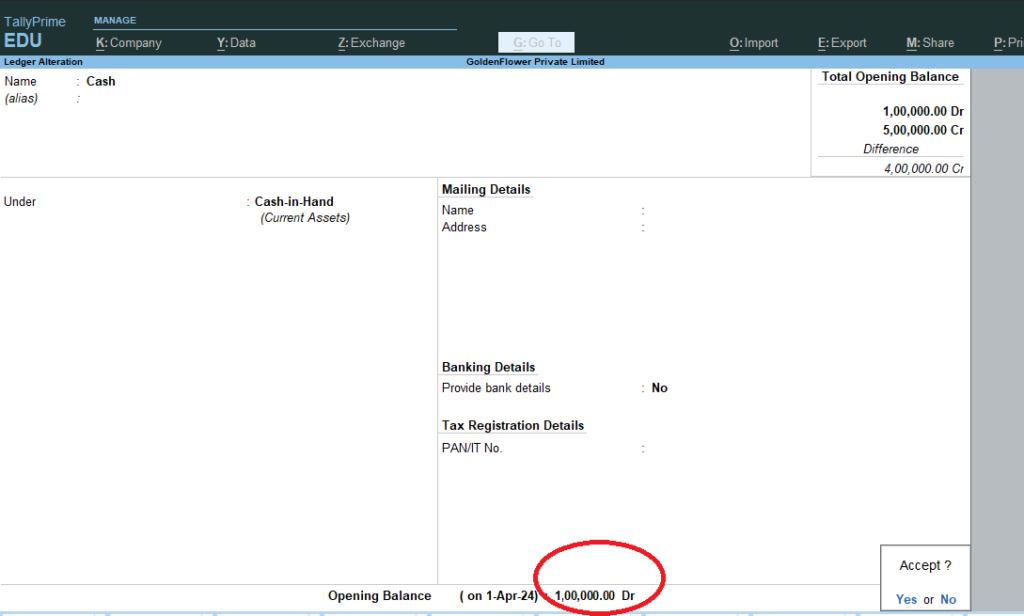
7) Now Press Escape again and again to see the Gateway of tally
Create the below ledgers using above steps >
Ledger Name Group Debit (₹) Credit (₹) SBI A/c Bank Accounts 2,00,000 Sales Sales Account 3,00,000 Purchase Purchase Account 1,50,000 Customer A Sundry Debtors 50,000 Supplier A Sundry Creditors 75,000 Office Equipment Fixed Assets 70,000 Salary Expenses Indirect Expenses 1,70,000 Rent Expenses Indirect Expenses 40,000 Outstanding Expenses Current Liabilities 20,000 Commission Received Indirect Incomes 25,000 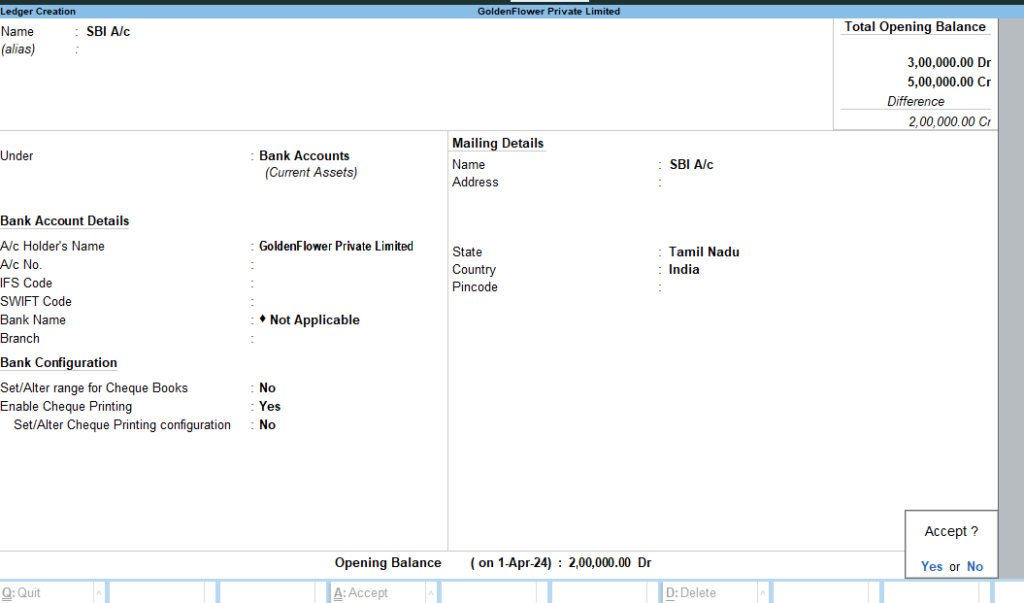
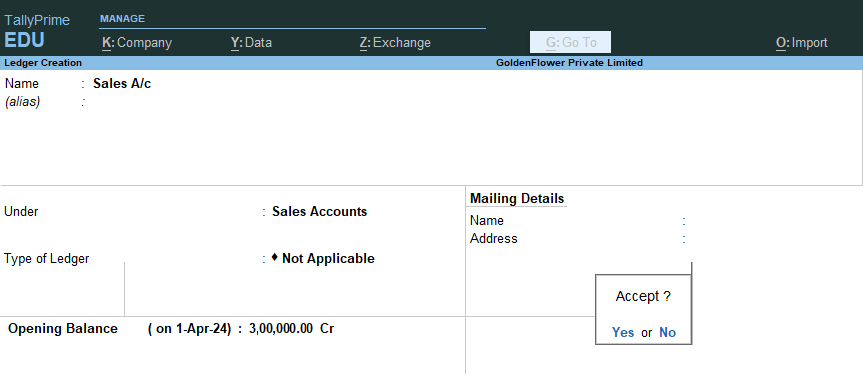
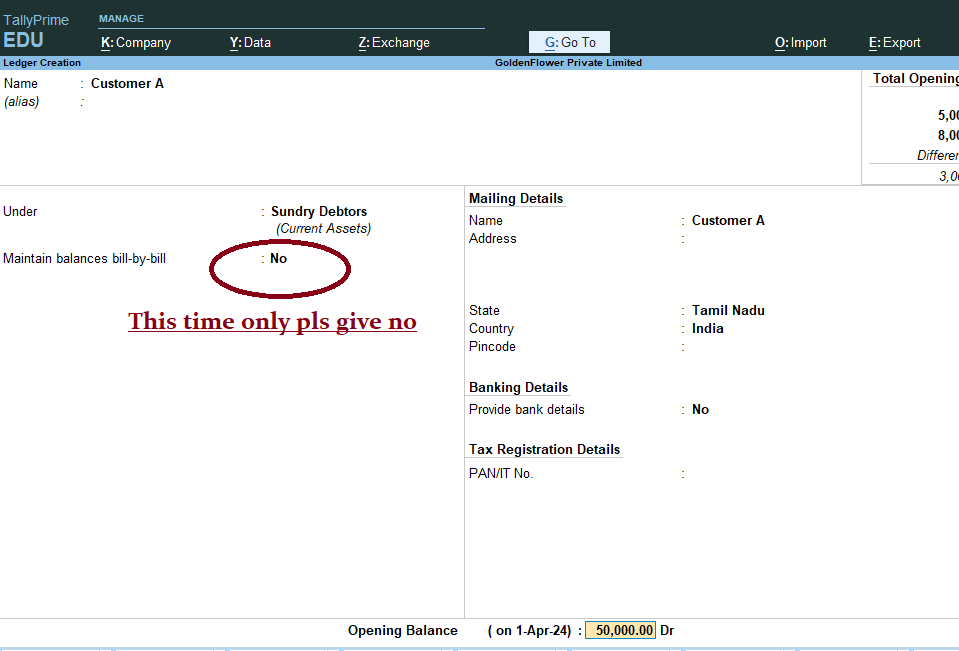
8) After Created the above all ledgers with Opening Balance as per trail balance
go Gateway of Tally > D: Display More Reports > T: Trail Balance >
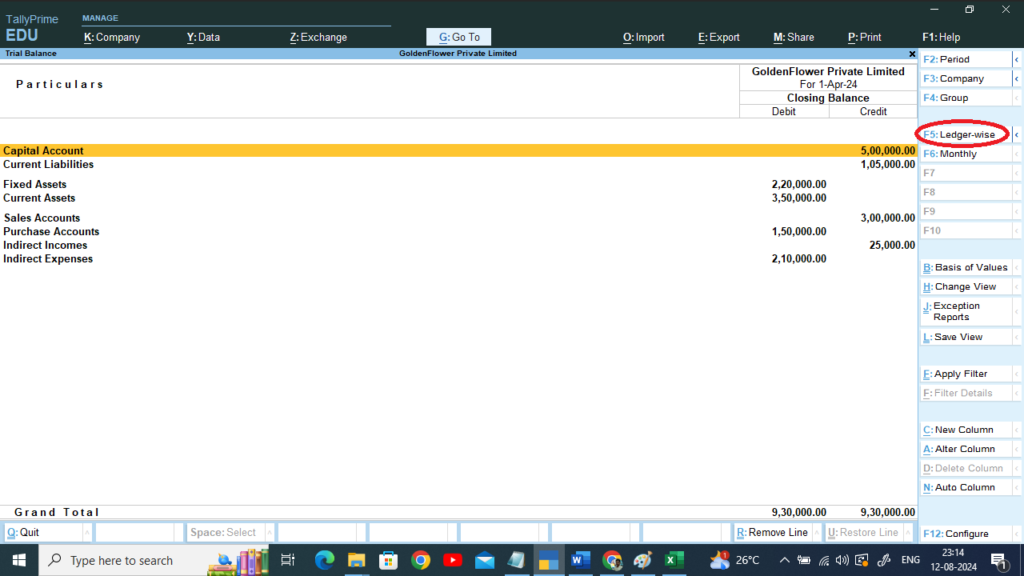
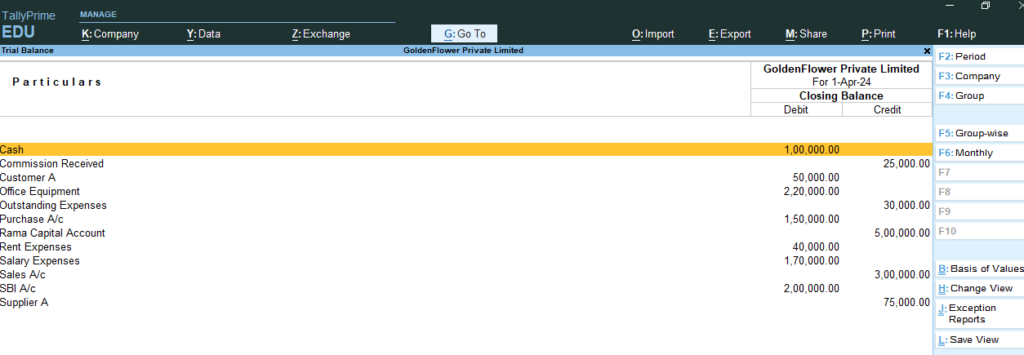
Press F5 > To See Ledger Wise >
9) Now Goto Gateway of Tally > Masters : Alter > Ledgers > Commission Received > Change the Opening Balance Amount : 80000 Accept > Yes
10) Now Goto Gateway of Tally > Masters : Alter > Ledgers > Cash > Change the Opening Balance Amount : 155000– Accept > Yes
11) go Gateway of Tally > D: Display More Reports > T: Trail Balance >
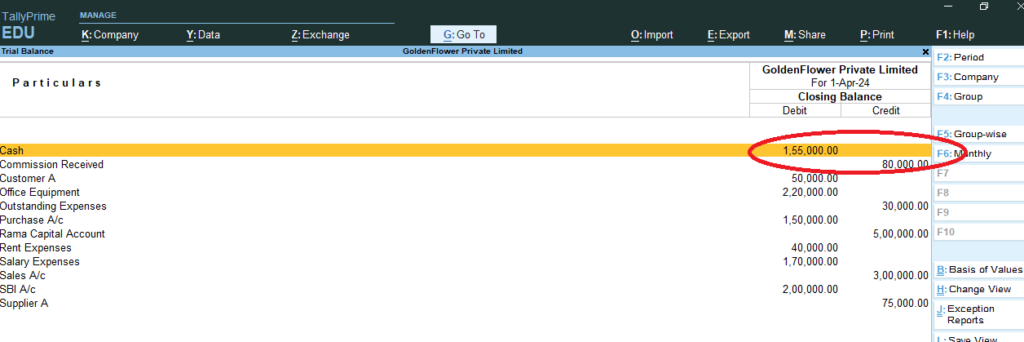
12) Gateway of Tally > Profit and Loss A/c
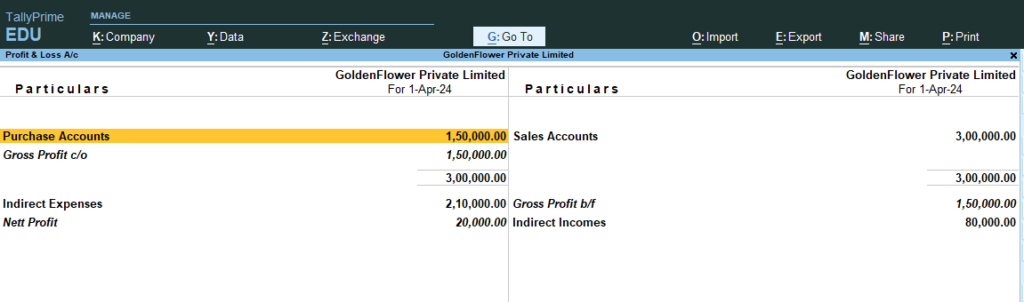
13) Gateway of Tally > Balance Sheet
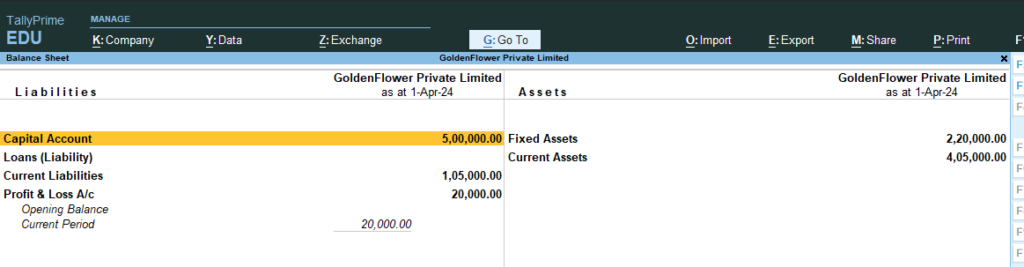
-
Tally Prime – Usage of Ledgers and Groups in Different Organizations
1) Service Oriented Organizations
For a service-oriented organization using Tally Prime, the ledger and group setup will focus on managing revenue from services, handling expenses, and tracking other financial activities specific to service-based operations. Here’s a structured approach for setting up these ledgers and groups:
1. Groups
Group Name Description Sundry Debtors Ledgers for clients or customers who owe payment for services rendered. Sundry Creditors Ledgers for suppliers or service providers. Income Revenues from various services provided. Expenses Various expenses including operational and administrative costs. Fixed Assets Assets such as office equipment and furniture. Cash Cash transactions and balances. Bank Transactions related to bank accounts. 2. Ledgers
Group Ledger Name Description Sundry Debtors Client A Receivables Ledger for a specific client who owes payment. Client B Receivables Ledger for another client. Sundry Creditors Supplier A Ledger for a specific supplier (e.g., office supplies). Service Provider A Ledger for service providers (e.g., IT support, consultancy). Income Service Income Revenue from the services provided (e.g., consulting fees). Project Income Revenue from specific projects or contracts. Other Income Other sources of income (e.g., interest, miscellaneous revenue). Expenses Salaries and Wages Salaries and wages for employees and contractors. Rent Expense for renting office space. Utilities Costs for utilities like electricity and water. Office Supplies Costs for office supplies and materials. Travel Expenses Costs related to travel for business purposes. Professional Fees Costs for professional services (e.g., legal, accounting). Fixed Assets Office Equipment Ledger for office equipment (e.g., computers, printers). Furniture Ledger for office furniture. Leasehold Improvements Ledger for improvements made to leased premises. Cash Petty Cash Small cash transactions and expenses. Bank Bank Account 1 Ledger for a specific bank account. Bank Account 2 Ledger for another bank account. This setup helps service-oriented organizations track their revenue from services, manage expenses related to operations, and maintain accurate records of financial transactions.
2) For retail or supermarkets
For retail or supermarkets using Tally Prime, organizing ledgers and groups in a table format can help manage various aspects of financial transactions and inventory. Here’s a structured view of how you might set up ledgers and groups for a retail or supermarket business:
1. Groups
Group Name Description Sundry Debtors Ledgers for customers who owe money for purchased goods. Sundry Creditors Ledgers for suppliers/vendors to whom payments are owed. Stock-in-Hand Manages inventory or stock. Sales Revenue from sales transactions. Purchases Costs related to buying inventory. Indirect Expenses Expenses not directly tied to goods sold (e.g., rent, utilities). Direct Expenses Expenses directly related to the purchase of inventory (e.g., freight). Fixed Assets Assets used in the business such as machinery and furniture. Cash Cash transactions and balances. Bank Transactions related to bank accounts. 2. Ledgers
Group Ledger Name Description Sundry Debtors Customer A Individual customer ledger. Customer B Another customer ledger. Sundry Creditors Supplier A Ledger for a specific supplier. Supplier B Ledger for another supplier. Stock-in-Hand Groceries Ledger for groceries stock. Electronics Ledger for electronic goods stock. Sales Cash Sales Revenue from cash sales. Credit Sales Revenue from sales on credit. Purchases Inventory Purchase Cost of purchasing inventory. Freight Charges Costs related to transporting goods. Indirect Expenses Rent Expense for renting store premises. Utilities Expenses for utilities like electricity and water. Office Supplies Costs for office-related supplies. Direct Expenses Purchase Freight Freight charges directly related to purchasing goods. Packaging Costs Costs for packaging materials. Fixed Assets Store Equipment Ledger for equipment like cash registers, shelves, etc. Furniture Ledger for store furniture. Cash Petty Cash Small cash transactions and expenses. Bank Bank Account 1 Ledger for a specific bank account. Bank Account 2 Ledger for another bank account. This setup will help you track sales, purchases, inventory, expenses, and bank transactions efficiently, making it easier to manage and report on the financial aspects of a retail or supermarket business.
3) For Manufacturing companies
For manufacturing companies using Tally Prime, the ledger and group setup will focus on tracking production costs, inventory, and other operational expenses. Here’s how you might organize these ledgers and groups in a table format:
1. Groups
Group Name Description Sundry Debtors Ledgers for customers who owe money for goods sold. Sundry Creditors Ledgers for suppliers/vendors from whom materials are purchased. Stock-in-Hand Manages inventory of raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods. Sales Revenue from sales of finished products. Purchases Costs related to buying raw materials and other inputs. Direct Expenses Expenses directly related to production (e.g., direct labor, raw materials). Indirect Expenses Expenses not directly tied to production (e.g., rent, utilities). Fixed Assets Assets used in manufacturing such as machinery and equipment. Cash Cash transactions and balances. Bank Transactions related to bank accounts. 2. Ledgers
Group Ledger Name Description Sundry Debtors Customer A Individual customer ledger. Customer B Another customer ledger. Sundry Creditors Supplier A Ledger for a specific supplier. Supplier B Ledger for another supplier. Stock-in-Hand Raw Materials Ledger for raw materials used in production. Work-in-Progress Ledger for partially completed products. Finished Goods Ledger for finished products ready for sale. Sales Domestic Sales Revenue from sales within the country. Export Sales Revenue from sales to other countries. Purchases Raw Material Purchases Cost of purchasing raw materials. Packing Material Purchases Cost of packing materials. Direct Expenses Direct Labor Wages and salaries directly tied to production. Production Supplies Costs for supplies used directly in manufacturing. Indirect Expenses Rent Expense for renting factory or office space. Utilities Costs for utilities such as electricity, water, etc. Administrative Expenses Costs related to administrative functions. Fixed Assets Machinery Ledger for machinery used in production. Equipment Ledger for production equipment. Cash Petty Cash Small cash transactions and expenses. Bank Bank Account 1 Ledger for a specific bank account. Bank Account 2 Ledger for another bank account. This setup helps track the various aspects of manufacturing operations, including inventory management, production costs, sales, and financial transactions, making it easier to manage and analyze financial data.
4) For schools and Collages
For schools using Tally Prime, the ledger and group setup will focus on managing finances related to tuition fees, salaries, utilities, and other school-related expenses. Here’s how you might organize these ledgers and groups in a table format:
1. Groups
Group Name Description Sundry Debtors Ledgers for students or parents who owe tuition fees. Sundry Creditors Ledgers for vendors or suppliers providing services or materials. Income Revenue from sources like tuition fees and donations. Expenses Various expenses incurred by the school. Fixed Assets Assets such as buildings, furniture, and equipment. Cash Cash transactions and balances. Bank Transactions related to bank accounts. 2. Ledgers
Group Ledger Name Description Sundry Debtors Student Fees Receivable Ledger for tracking tuition fees owed by students. Parent Fees Receivable Ledger for fees receivable from parents. Sundry Creditors Supplier A Ledger for a specific supplier (e.g., stationery supplier). Service Provider A Ledger for service providers (e.g., cleaning services). Income Tuition Fees Revenue from student tuition fees. Donations Income from donations and grants. Miscellaneous Income Other sources of income (e.g., event fees). Expenses Salaries and Wages Salaries and wages for teachers and staff. Utilities Expenses for electricity, water, and other utilities. Stationery and Supplies Costs for educational supplies and stationery. Maintenance Costs Expenses for maintaining school facilities. Fixed Assets Building Ledger for school buildings and property. Furniture and Fixtures Ledger for classroom and office furniture. Educational Equipment Ledger for equipment like computers, projectors, etc. Cash Petty Cash Small cash transactions and expenses. Bank Bank Account 1 Ledger for a specific bank account. Bank Account 2 Ledger for another bank account. This setup helps schools manage their financial transactions efficiently, including tracking income from tuition fees, managing expenses related to operations, and handling bank and cash transactions.
5) For government organizations
For government organizations using Tally Prime, the ledger and group setup will focus on managing public funds, tracking expenditures, handling revenues, and maintaining transparency. Here’s a structured approach for setting up these ledgers and groups:
1. Groups
Group Name Description Sundry Debtors Ledgers for receivables from other government entities or departments. Sundry Creditors Ledgers for payments owed to suppliers and contractors. Income Revenues from various sources such as grants, taxes, and fees. Expenditure Various expenditures including operational and project costs. Fixed Assets Assets like buildings, equipment, and infrastructure. Cash Cash transactions and balances. Bank Transactions related to bank accounts. 2. Ledgers
Group Ledger Name Description Sundry Debtors Receivables from Department A Amounts receivable from other government departments. Receivables from External Agencies Amounts receivable from external entities or agencies. Sundry Creditors Supplier A Ledger for a specific supplier or contractor. Service Provider A Ledger for service providers (e.g., maintenance services). Income Grants and Subsidies Revenue from grants and subsidies provided by higher authorities. Tax Revenues Revenues from various taxes (e.g., property tax, sales tax). Fees and Charges Income from fees for services provided (e.g., registration fees). Expenditure Salaries and Wages Salaries and wages for employees and officials. Operational Expenses Day-to-day operational costs (e.g., utilities, office supplies). Project Expenses Costs related to specific government projects or initiatives. Maintenance Costs Expenses for maintaining government properties and equipment. Fixed Assets Buildings Ledger for government buildings and infrastructure. Office Equipment Ledger for office equipment and furniture. Vehicles Ledger for government vehicles. Cash Petty Cash Small cash transactions and expenditures. Bank Bank Account 1 Ledger for a specific bank account. Bank Account 2 Ledger for another bank account. This setup ensures that government organizations can effectively manage their finances, track revenue and expenditures, and maintain transparency and accountability in their financial reporting.
6) For municipalities, corporations, or town panchayats
For municipalities, corporations, or town panchayats using Tally Prime, the ledger and group setup will help manage public funds, track expenditures, and handle various local government functions. Here’s how you might organize these ledgers and groups:
1. Groups
Group Name Description Sundry Debtors Ledgers for amounts receivable from residents and businesses (e.g., property tax arrears). Sundry Creditors Ledgers for payments owed to suppliers, contractors, and service providers. Income Revenues from various sources such as taxes, fees, and grants. Expenditure Various expenditures including operational costs and project expenses. Fixed Assets Assets like buildings, equipment, and infrastructure. Cash Cash transactions and balances. Bank Transactions related to bank accounts. 2. Ledgers
Group Ledger Name Description Sundry Debtors Property Tax Receivables Amounts receivable from property owners for taxes. Water Charges Receivable Amounts receivable from residents for water charges. Municipal Fees Receivable Amounts receivable from various municipal services. Sundry Creditors Supplier A Ledger for a specific supplier (e.g., for materials or services). Contractor A Ledger for contractors providing construction or maintenance services. Service Provider A Ledger for service providers (e.g., waste management, street cleaning). Income Property Tax Income Revenue from property taxes. Water Revenue Revenue from water charges. Service Fees Income from various municipal services (e.g., permits, licenses). Grants and Subsidies Income from grants and subsidies received from higher authorities. Expenditure Salaries and Wages Salaries and wages for municipal employees. Operational Expenses Day-to-day operational costs (e.g., utilities, office supplies). Maintenance Costs Costs for maintaining public infrastructure and facilities. Project Expenses Expenses for specific municipal projects (e.g., road construction). Fixed Assets Buildings Ledger for municipal buildings and facilities. Street Lighting Ledger for street lighting infrastructure. Public Equipment Ledger for equipment used for public services (e.g., vehicles). Cash Petty Cash Small cash transactions and expenditures. Bank Bank Account 1 Ledger for a specific bank account. Bank Account 2 Ledger for another bank account. This setup will help municipalities, corporations, or town panchayats manage their financial activities efficiently, track income and expenditures, and maintain effective control over public funds and assets.
7) For trading companies
For trading companies using Tally Prime, the ledger and group setup will focus on managing inventory, sales, purchases, and related financial transactions. Here’s how you might organize these ledgers and groups:
1. Groups
Group Name Description Sundry Debtors Ledgers for customers who owe money for goods sold. Sundry Creditors Ledgers for suppliers from whom inventory is purchased. Stock-in-Hand Manages inventory of goods for resale. Sales Revenue from sales transactions. Purchases Costs related to buying inventory. Direct Expenses Expenses directly tied to the procurement and sale of goods. Indirect Expenses Expenses not directly tied to the sale of goods (e.g., rent, utilities). Fixed Assets Assets such as buildings, furniture, and equipment. Cash Cash transactions and balances. Bank Transactions related to bank accounts. 2. Ledgers
Group Ledger Name Description Sundry Debtors Customer A Ledger for a specific customer. Customer B Ledger for another customer. Sundry Creditors Supplier A Ledger for a specific supplier. Supplier B Ledger for another supplier. Stock-in-Hand Inventory – Goods Ledger for tracking goods available for sale. Raw Materials Ledger for raw materials if involved in manufacturing. Sales Domestic Sales Revenue from sales within the country. Export Sales Revenue from sales to other countries. Purchases Inventory Purchases Cost of purchasing goods for resale. Freight Charges Cost of transporting goods. Direct Expenses Purchase Expenses Costs directly related to purchasing inventory (e.g., freight, handling). Packaging Costs Costs for packaging materials. Indirect Expenses Rent Expense for renting office or warehouse space. Utilities Costs for utilities such as electricity and water. Office Supplies Costs for office-related supplies. Advertising Costs for advertising and marketing. Fixed Assets Building Ledger for buildings and real estate. Furniture and Fixtures Ledger for office furniture and fixtures. Equipment Ledger for machinery and other equipment. Cash Petty Cash Small cash transactions and expenditures. Bank Bank Account 1 Ledger for a specific bank account. Bank Account 2 Ledger for another bank account. This setup will help trading companies manage their financial transactions effectively, keep track of inventory and sales, and handle both direct and indirect expenses.
-
Type of Organizations
Organizations can be classified into various types based on their structure, ownership, and objectives. Here’s an overview of different types of organizations:
- Sole Proprietorship
Description: Owned and operated by a single individual.
Characteristics: Simple to set up, owner has complete control, unlimited liability.
Examples: Local small businesses, freelance professionals. - Partnership
Description: Owned by two or more individuals who share profits and responsibilities.
Characteristics: Shared management, limited liability (in limited partnerships), profits and losses shared as per the partnership agreement.
Examples: Law firms, accounting firms, medical practices. - Limited Liability Partnership (LLP)
Description: A partnership where some or all partners have limited liabilities.
Characteristics: Combines elements of partnerships and corporations, protects individual partners from personal liability.
Examples: Professional services firms, startups. - Private Limited Company (Ltd)
Description: A privately held company with limited liability.
Characteristics: Owned by a small group of investors, shares are not publicly traded, limited liability for shareholders.
Examples: Small to medium-sized enterprises, family businesses. - Public Limited Company (PLC)
Description: A company whose shares are traded on a stock exchange and are available to the public.
Characteristics: Limited liability, can raise capital by issuing shares, regulated by stock exchange laws.
Examples: Large corporations like Apple, Microsoft. - Non-Profit Organization (NPO)
Description: An organization that operates for charitable, educational, or other socially beneficial purposes rather than for profit.
Characteristics: Exempt from income taxes, must reinvest surplus funds into the organization’s mission.
Examples: Charities, foundations, educational institutions. - Cooperative
Description: An organization owned and operated by its members, who share the profits or benefits.
Characteristics: Members have equal voting rights, profits are distributed among members.
Examples: Agricultural cooperatives, credit unions, housing cooperatives. - Government Organization
Description: Entities created and operated by the government to provide public services.
Characteristics: Funded by taxpayer money, not-for-profit, serves public interests.
Examples: Public schools, municipal services, government agencies. - State-Owned Enterprise (SOE)
Description: A business owned and operated by the government.
Characteristics: May operate like a private corporation but is controlled by government policies.
Examples: National airlines, utilities companies. - Joint Venture
Description: A business arrangement where two or more parties agree to pool their resources for a specific project or purpose.
Characteristics: Shared risk and reward, separate legal entity, typically for a limited time.
Examples: Collaborative projects between companies, international business collaborations. - Franchise
Description: A business model where an individual or group is granted the right to operate a business using the branding and business model of an established company.
Characteristics: Franchisee operates independently but under the franchisor’s brand and guidelines.
Examples: Fast-food chains like McDonald’s, retail stores like 7-Eleven. - Social Enterprise
Description: An organization that applies commercial strategies to maximize improvements in human and environmental well-being.
Characteristics: Focuses on social impact rather than profit, often reinvests profits to achieve social goals.
Examples: Fair trade companies, businesses addressing social issues. - Mutual Benefit Association
Description: An organization formed to provide benefits to its members, such as insurance or financial support.
Characteristics: Members contribute to a common fund and receive benefits based on their contributions.
Examples: Insurance companies, professional associations.
Summary
These types of organizations vary widely in their structure, purpose, and operational characteristics, and understanding these differences can help in recognizing their unique roles in the economy and society.
- Sole Proprietorship
