- Tally Prime Installation
- Tally Prime – Accounts – Basic – Tamil
- Tally Prime இல் Ledger உருவாக்குவது எப்படி – Example 1
- Tally Prime இல் Ledger உருவாக்குவது எப்படி – Example 2
- Tally Accounting Software – Simple Voucher Entry
- Tally Prime இல் Accounting Vouchers – Part 1 | Tally Prime Tutorial in Tamil”
- Learn Tally Prime in Tamil | Inventory Management | How Create Stock Item, Groups,Category and Units
- Tally Prime Tutorial in Tamil | Inventory | How Create Stock Item, Group, Category, Location
Tag: Tally Ledgers
-
Learn Tally Prime – Tamil Tutorials Videos Links
-
Tally Prime – Step by Step to Create Ledgers – Example 1
- First Create a new company named Royal Trading & Co
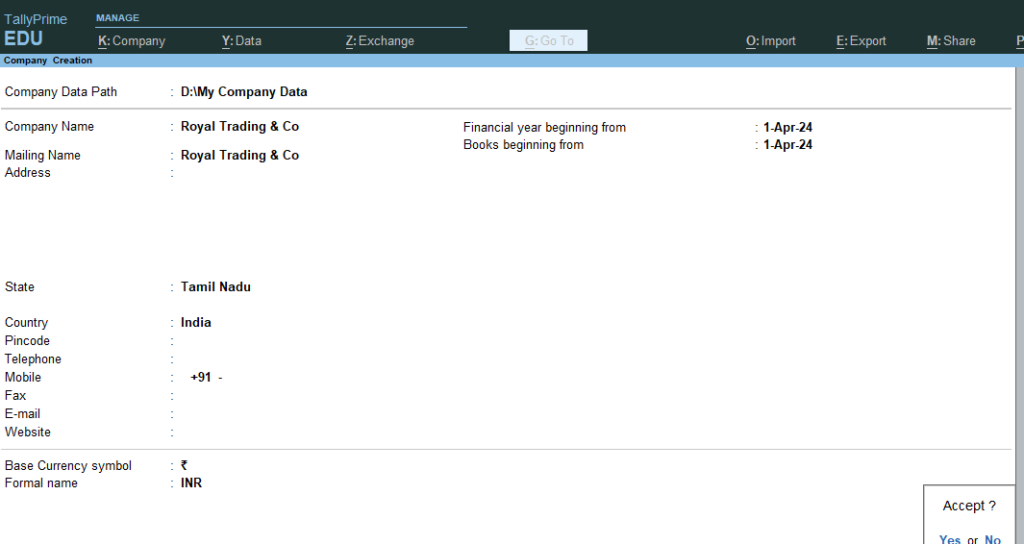
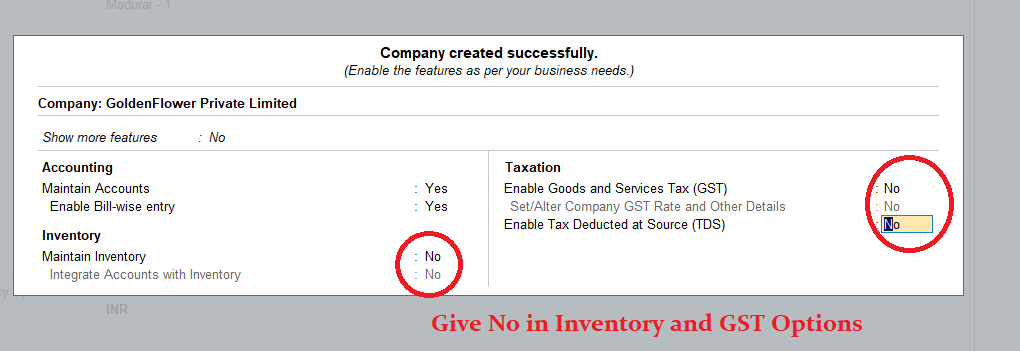
2. After Company Creation > First Create the following ledgers >
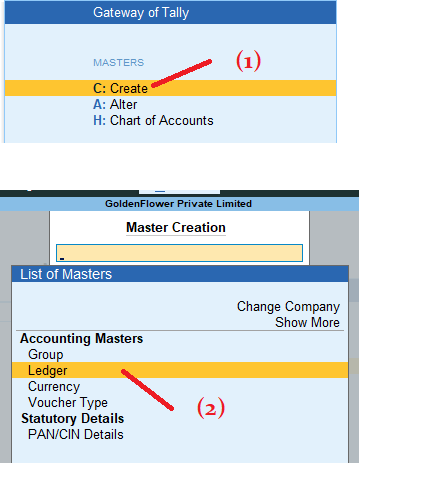
Ledger Name Group Debit (₹) Credit (₹) Ramu Capital Account Capital Account 10000 Cash in Hand Cash-in-Hand 10000 3. Gateway of Tally > Masters : Create > Ledgers:
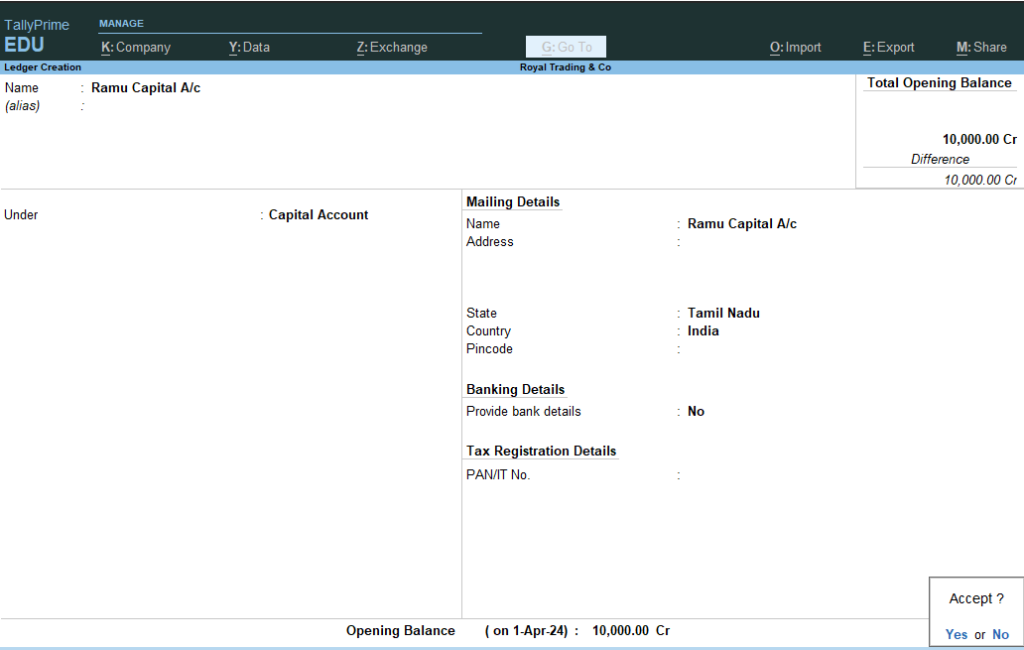
4. Enter Name : Ramu Capital A/c — Under : Type Cap and Select Right Side Using Arrow Keys or Select and Enter Capital Account > and Give Opening Balance : 10000 Cr. > Accept Yes >
5. Now you will see the Same Ledger creation > Press Escape twice and Goto Gateway of Tally >
6. Gateway of Tally > Master : Alter > Ledgers > Select Cash > Opening Balance : 10000 Dr.
7. So Ramu is Giver and Cash is Comes in to Business . So Cr. Ramu Capital A/c and Dr. Cash A/c
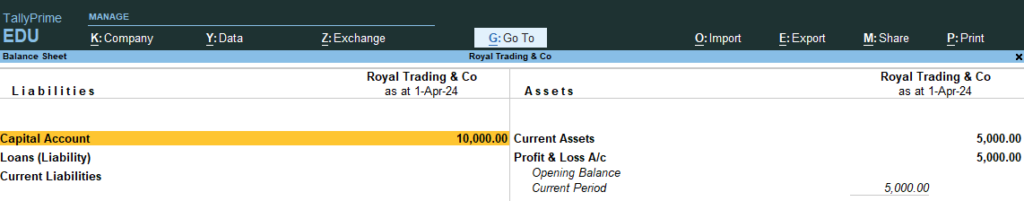
8. Go Gateway of Tally > Go Balance Sheet > You Can See Liabilities / Current Assets Statement
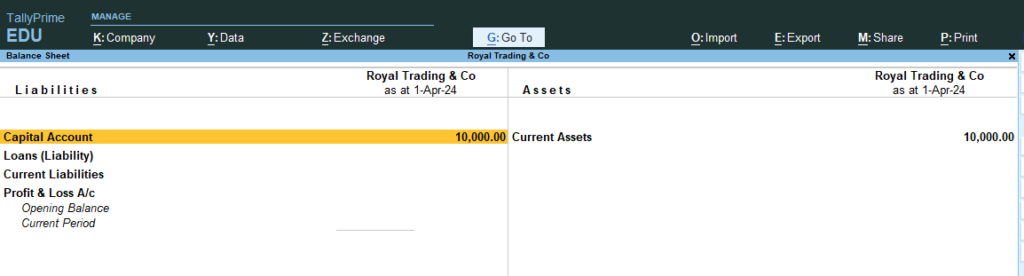
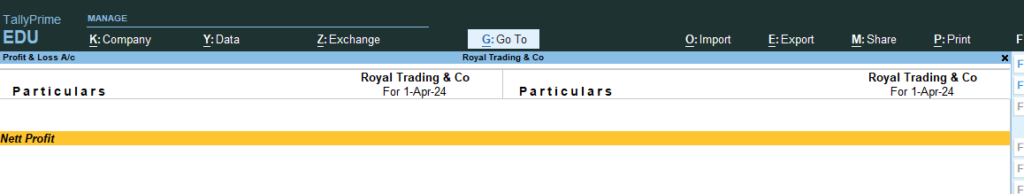
9. Go Gateway of Tally > Go Profit and Loss A/c > No Profit and Loss Data because no entry made in any purchase or sales
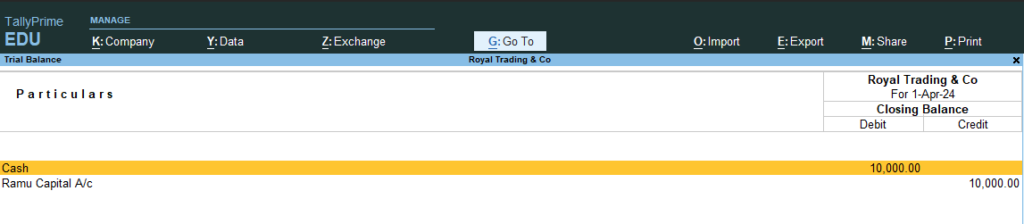
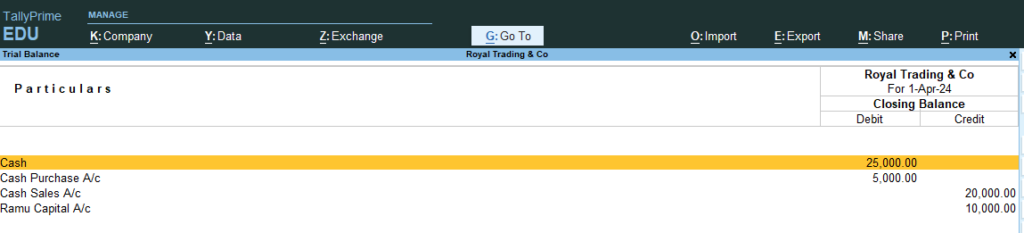
10. Go Gateway of Tally > Go Display More Reports or Press D > Go Trail Balance > and Press F5 (Ledger Wise / Group wise breakup)
11. Now Add the following Ledger
Ledger Name Group Debit (₹) Credit (₹) Cash Purchase A/c Purchase 5000 Go Gateway of Tally > Enter Name : Cash Purchase A/c — Under : Select Purchase Account > and Give Opening Balance : 5000 Cr. > Accept Yes >
Gateway of Tally > Master : Alter > Ledgers > Select Cash > Opening Balance : 5000 Dr. (Because Amount to be reduced due to Cash purchase Rs.5000)
12. Now Go the Step No 8 , 9, 10 (See the changes in Profit and Loss and Balance sheet , now net loss Because Only Cash Purchase Not Sales ..)
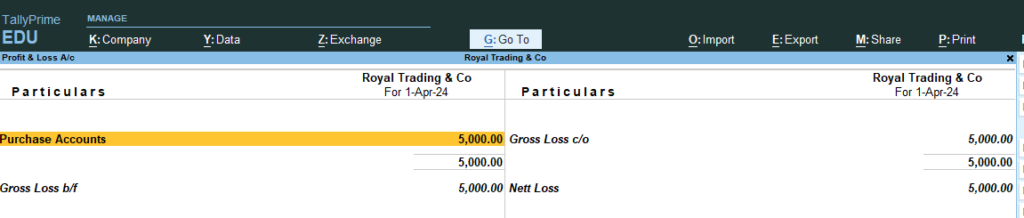
13. Now Add the following Ledger
Ledger Name Group Debit (₹) Credit (₹) Cash Sales A/c Sales 20000 Go Gateway of Tally > Master > Create : Ledgers > Enter Name : Cash Sales A/c — Under : Select Sales Account > and Give Opening Balance : 20000 Dr. > Accept Yes >
Gateway of Tally > Master : Alter > Ledgers > Select Cash > Opening Balance : 25000 Dr. (Because Amount to be raised due to Cash Sales Rs.20000)
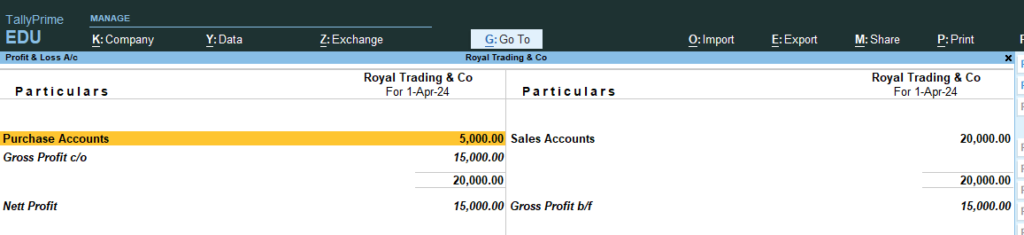
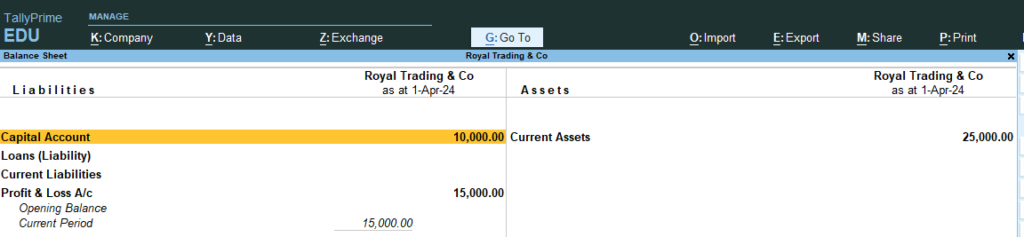
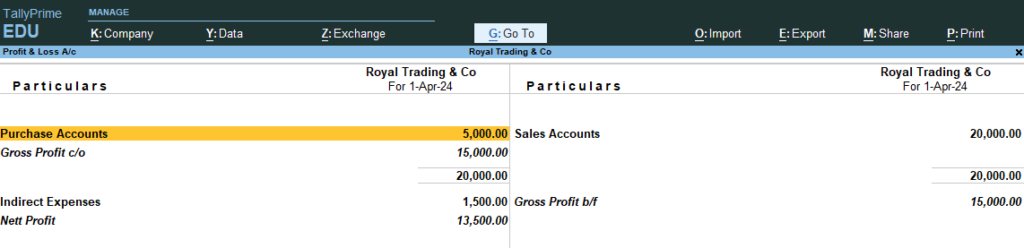
14. Now Go the Step No 8 , 9, 10 (See the changes in Profit and Loss and Balance sheet)
Profit and Loss A/c
Balance Sheet
Trail Balance
13. Now Add the following Ledger
Ledger Name Group Debit (₹) Credit (₹) Furniture Fixed Asset 5000 Telephone Charges Indirect Expenses 1000 Electricity Bill Paid Indirect Expenses 500 Total 6500 14. Go Gateway of Tally > Master > Create : Ledgers > Name : Furniture — Under : Fixed Asset > and Give Opening Balance : 5000 Dr. > Accept Yes >
15. Name : Telephone Charges — Under : Indirect Expenses > and Give Opening Balance : 1000 Dr.
16. Name : Electricity Bill Paid — Under : Indirect Expenses > and Give Opening Balance : 500 Dr.
17, Gateway of Tally > Master : Alter > Ledgers > Select Cash > Opening Balance : 18500 Dr. (Because Amount to be reduced due to Expenses (25000- 6500 = 18500 Dr.)
18. Now Go the Step No 8 , 9, 10 (See the changes in Profit and Loss and Balance sheet)
If any doubt say comments … thanks
Continue…..
-
Tally Prime – Ledgers and Groups
What is a Ledger?
- Ledger is like a detailed record or account that tracks all transactions related to a specific item or entity.
- Think of it as a notebook where you write down everything that happens related to one thing, like all the money you spend on rent or all the sales you make.
Examples:
- Cash Ledger: Tracks all cash transactions (money coming in and going out).
- Sales Ledger: Tracks all the sales made by the business.
- Salary Ledger: Tracks the payments made to employees.
What is a Group?
- Group is a category that helps organize ledgers in Tally Prime.
- It’s like a folder where similar types of ledgers are kept together. This makes it easier to manage and find them.
- Groups help Tally Prime understand what kind of transactions are recorded in each ledger.
Examples:
- Capital Account: This is a group of ledgers involving owners’ investment in the business.
- Sundry Debtors: These are the various individuals or firms from whom the business has to recover.
- Fixed Assets: A group containing ledgers for items owned by the business, like furniture or any type of machinery.
Why Use Ledgers and Groups?
- Organized Record-Keeping: By using ledgers and groups, you can keep your financial records organized and easy to understand.
- Accurate Reporting: Tally Prime can generate accurate financial reports, like balance sheets and profit & loss statements, based on the information in ledgers.
- Simplifies Management: Groups help you manage similar accounts together, making it easier to analyze the financial health of the business.
Ledgers as a Diary:
This is how one can understand what a ledger is. A ledger is just like a diary where one writes everything concerning a particular subject. For example, you have a daily journal where you write down all your daily expenses. For example, you have a daily journal in which you write down all your expenses each day. Every page may be allocated to various spends one makes, such as food, travel, or entertainment.
Groups as Categories:
Now, these pages in your diary will be divided based on sections or categories. For example, you can have “Food,” another “Travel,” and another “Entertainment.” Then within each category, there are those sheets of pages where you write down the specifics.
In accounting, these categories are termed “Groups”, with the sheets being “Ledgers.”
Example:For example, one group could be “Expenses,” while sub-ledgers might include “Rent,” “Groceries,” or “Utilities.” All the transactions related to each particular expense would then be noted in its corresponding ledger.
Expenses (Group)
├── Rent (Ledger)
├── Salary (Ledger)
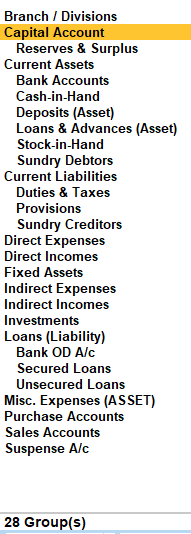
└── Utilities (Ledger)In Tally Prime, there are a total of 28 predefined groups. These groups are used to classify and organize ledgers according to their nature and purpose. Here’s a breakdown:
15 Primary Groups
These are the main groups under which all other groups and ledgers are classified.
- Capital Account
- Reserves & Surplus
- Loans (Liability)
- Current Liabilities
- Current Assets
- Fixed Assets
- Investments
- Branch/Divisions
- Miscellaneous Expenses (Asset)
- Suspense Account
- Sales Accounts
- Purchase Accounts
- Direct Incomes
- Direct Expenses
- Indirect Incomes
13 Subgroups
These subgroups are categorized under the primary groups:
- Sundry Creditors (Under Current Liabilities)
- Sundry Debtors (Under Current Assets)
- Cash-in-Hand (Under Current Assets)
- Bank Accounts (Under Current Assets)
- Loans & Advances (Asset) (Under Current Assets)
- Duties & Taxes (Under Current Liabilities)
- Provisions (Under Current Liabilities)
- Stock-in-Hand (Under Current Assets)
- Deposits (Asset) (Under Current Assets)
- Secured Loans (Under Loans (Liability))
- Unsecured Loans (Under Loans (Liability))
- Branch/Division (Under Capital Account)
- Suspense Account (Under Current Liabilities)
Custom Groups
- You can also create custom groups based on specific business needs. These custom groups can be placed under any of the primary groups listed above.
Activity :
After Company Creation > Gateway to Tally > Under Masters > H: Chart of Accounts > Groups :
Here’s a detailed explanation of all 28 groups in Tally Prime, along with examples of ledgers that fall under each group:
1. Capital Account
- Purpose: Tracks the owner’s equity or investment in the business and any withdrawals.
- Examples:
- Capital Ledger: Represents the owner’s investment.
- Drawings Ledger: Tracks money withdrawn by the owner for personal use.
- Amutha Capital a/c
- Owner Name Capital A/c
2. Reserves & Surplus
- Purpose: Represents accumulated profits retained in the business or any reserves.
- Examples:
- General Reserve Ledger: A reserve fund for future contingencies.
- Profit & Loss Account: If there’s a profit carried forward from previous years.
3. Loans (Liability)
- Purpose: Tracks borrowed funds that the business needs to repay.
- Examples:
- Bank Loan Ledger: Records loans taken from banks.
- Debenture Ledger: Tracks money raised through debentures.
4. Current Liabilities
- Purpose: Represents short-term obligations or debts that the business must pay within a year.
- Examples:
- Sundry Creditors Ledger: Money owed to suppliers or vendors.
- Outstanding Expenses Ledger: Expenses that have been incurred but not yet paid.
5. Current Assets
- Purpose: Represents assets that can be converted into cash within a year.
- Examples:
- Sundry Debtors Ledger: Tracks amounts receivable from customers.
- Cash Ledger: Records all cash transactions.
6. Fixed Assets
- Purpose: Represents long-term assets that the business owns, like property, machinery, etc.
- Examples:
- Building Ledger: Tracks the value of buildings owned.
- Machinery Ledger: Represents the value of machinery used in the business.
7. Investments
- Purpose: Tracks investments made by the business in other companies, stocks, bonds, etc.
- Examples:
- Shares Ledger: Records the purchase of shares in other companies.
- Government Bonds Ledger: Tracks investments in government bonds.
8. Branch/Divisions
- Purpose: Used to track accounts for different branches or divisions within the same company.
- Examples:
- Branch A Ledger: Records transactions specific to Branch A.
- Division 1 Ledger: Tracks transactions related to a specific division within the company.
9. Miscellaneous Expenses (Asset)
- Purpose: Represents expenses that are deferred and written off over a period of time.
- Examples:
- Preliminary Expenses Ledger: Records expenses incurred during the formation of the company.
- Deferred Revenue Expenditure Ledger: Expenses to be written off gradually.
10. Suspense Account
- Purpose: Used temporarily for transactions where the correct ledger is not yet determined.
- Examples:
- Suspense Ledger: Any uncertain or incomplete transactions are recorded here temporarily.
11. Sales Accounts
- Purpose: Tracks income earned from selling goods or services.
- Examples:
- Domestic Sales Ledger: Records sales made within the country.
- Export Sales Ledger: Tracks sales made to customers outside the country.
- Sales A/c
- Cash Sales A/c
- Credit Sales A/c
12. Purchase Accounts
- Purpose: Tracks the cost of goods or services purchased by the business.
- Examples:
- Local Purchases Ledger: Records purchases made from local suppliers.
- Import Purchases Ledger: Tracks purchases made from foreign suppliers.
- Purchase A/c
- Cash Purchase A/c
- Cash Sales A/c
- Purchase Return A/c
13. Direct Incomes
- Purpose: Represents income directly related to the core business activities.
- Examples:
- Commission Received Ledger: Tracks commission earned from sales.
- Service Income Ledger: Records income from services provided.
- Professional Charges A/c
- Consulting Fees A/c
- Service Charges A/c
14. Direct Expenses
- Purpose: Represents expenses directly related to the production or purchase of goods.
- Examples:
- Freight Inwards Ledger: Tracks transportation costs for bringing goods into the business.
- Raw Material Ledger: Records the cost of raw materials used in production.
- Carriage inwards A/c
- Wages A/c
15. Indirect Incomes
- Purpose: Represents income from activities not directly related to the primary business operations.
- Examples:
- Interest Received Ledger: Tracks interest earned on deposits or investments.
- Rental Income Ledger: Records income from renting out property or equipment.
- Rent Received A/c
- Interest Received A/c
- Commission Received A/c
16. Indirect Expenses
- Purpose: Represents expenses not directly related to the production of goods but necessary for running the business.
- Examples:
- Rent Ledger: Tracks payments made for renting office space.
- Salary Ledger: Records payments made to employees.
- Telephone Charges A/c
- Bank Charges A/c
- Rent Charges A/c
- Electricity Expenses
17. Sundry Creditors (Under Current Liabilities)
- Purpose: Tracks amounts owed to suppliers or vendors.
- Examples:
- Raja Suppliers Ledger: Records money owed to Raja Suppliers.
- Kumar Traders Ledger: Tracks amounts payable to Kumar Traders.
- Balram A/c
- Rajan A/c
18. Sundry Debtors (Under Current Assets)
- Purpose: Tracks money receivable from customers who purchased goods or services on credit.
- Examples:
- Suresh & Co Customer Ledger: Records amounts receivable from Customer Suresh & Co
- Ramu A/c Ledger: Tracks money owed by Ramu A/c
19. Cash-in-Hand (Under Current Assets)
- Purpose: Tracks all cash transactions of the business.
- Examples:
- Main Cash Ledger: Records cash held by the business.
- Petty Cash Ledger: Tracks small cash expenses.
20. Bank Accounts (Under Current Assets)
- Purpose: Tracks all transactions related to bank accounts.
- Examples:
- HDFC Bank Ledger: Records transactions with HDFC Bank.
- ICICI Bank Ledger: Tracks transactions with ICICI Bank.
21. Loans & Advances (Asset) (Under Current Assets)
- Purpose: Represents loans given by the business to others.
- Examples:
- Advance to Supplier Ledger: Records advance payments made to suppliers.
- Loan to Employee Ledger: Tracks loans given to employees.
22. Duties & Taxes (Under Current Liabilities)
- Purpose: Tracks amounts related to taxes and duties payable to the government.
- Examples:
- GST Ledger: Records Goods and Services Tax collected and payable.
- Income Tax Ledger: Tracks the business’s income tax liability.
23. Provisions (Under Current Liabilities)
- Purpose: Represents amounts set aside for future expenses or liabilities.
- Examples:
- Provision for Taxation Ledger: Tracks amounts set aside for tax payments.
- Provision for Doubtful Debts Ledger: Records provisions made for bad debts.
24. Stock-in-Hand (Under Current Assets)
- Purpose: Tracks the value of goods in stock.
- Examples:
- Finished Goods Ledger: Records the value of finished goods in inventory.
- Raw Materials Ledger: Tracks the value of raw materials in stock.
25. Deposits (Asset) (Under Current Assets)
- Purpose: Represents deposits made by the business that are expected to be returned.
- Examples:
- Security Deposit Ledger: Tracks deposits given for securing premises or equipment.
- Fixed Deposit Ledger: Records fixed deposits made with banks.
26. Secured Loans (Under Loans (Liability))
- Purpose: Tracks loans that are backed by collateral or security.
- Examples:
- Mortgage Loan Ledger: Records loans taken against property.
- Car Loan Ledger: Tracks loans secured against a vehicle.
27. Unsecured Loans (Under Loans (Liability))
- Purpose: Tracks loans that are not backed by any collateral.
- Examples:
- Personal Loan Ledger: Records personal loans taken by the business.
- Overdraft Ledger: Tracks overdraft facilities provided by banks.
28. Branch/Division (Under Capital Account)
- Purpose: Tracks accounts for different branches or divisions within the same company.
- Examples:
- Branch A Capital Ledger: Records the capital allocated to Branch A.
- Division 1 Capital Ledger: Tracks the capital allocated to a specific division.
Group Ledger Name Purpose Capital Account Capital Owner’s investment in the business. Capital Account Drawings Owner’s withdrawals for personal use. Capital Account Partner A Capital Capital contribution by Partner A. Capital Account Partner B Capital Capital contribution by Partner B. Reserves & Surplus General Reserve Accumulated profits set aside for future use. Reserves & Surplus Profit & Loss A/C Profits or losses carried forward. Reserves & Surplus Retained Earnings Profits retained in the business. Reserves & Surplus Dividend Reserve Amount reserved for dividend distribution. Loans (Liability) Bank Loan Loans taken from banks. Loans (Liability) Debentures Funds raised through debentures. Loans (Liability) Loan from Directors Loans taken from company directors. Loans (Liability) Mortgage Loan Loans secured against property. Current Liabilities Sundry Creditors Amounts payable to suppliers or vendors. Current Liabilities Outstanding Expenses Expenses incurred but not yet paid. Current Liabilities Duties & Taxes Taxes payable (e.g., GST, VAT). Current Liabilities Salary Payable Salaries due but not yet paid. Current Liabilities TDS Payable Tax Deducted at Source yet to be paid to the government. Current Liabilities GST Payable Goods and Services Tax payable. Current Liabilities Professional Tax Payable Professional tax due for payment. Current Liabilities Provident Fund Payable Provident fund contributions due. Current Assets Sundry Debtors Money receivable from customers. Current Assets Cash Tracks all cash transactions. Current Assets HDFC Bank A/C Transactions related to HDFC Bank. Current Assets ICICI Bank A/C Transactions related to ICICI Bank. Current Assets Advance to Suppliers Payments made in advance to suppliers. Current Assets Prepaid Insurance Insurance premiums paid in advance. Current Assets Prepaid Rent Rent paid in advance. Current Assets Petty Cash Small cash expenses. Current Assets Advances to Employees Money advanced to employees. Current Assets Bills Receivable Bills that are due for payment from customers. Current Assets Fixed Deposit Money deposited in fixed-term accounts. Current Assets Investments in Shares Investments in company shares. Fixed Assets Building Value of buildings owned by the business. Fixed Assets Machinery Value of machinery used in the business. Fixed Assets Furniture & Fixtures Value of office furniture and fixtures. Fixed Assets Computers Value of computers and IT equipment. Fixed Assets Vehicles Value of vehicles owned by the business. Fixed Assets Office Equipment Value of office equipment (e.g., printers, fax machines). Fixed Assets Land Value of land owned by the business. Fixed Assets Air Conditioning Equipment Value of AC units installed in the office. Fixed Assets Tools & Equipment Value of tools used in manufacturing or operations. Investments Shares in ABC Ltd. Investment in shares of ABC Ltd. Investments Mutual Funds Investments in mutual funds. Investments Government Bonds Investments in government bonds. Investments Fixed Deposits Fixed deposits with banks. Investments Real Estate Investment Investments in real estate properties. Investments Investment in Subsidiary Company Investment in a subsidiary company. Investments Investment in Partnership Firm Investments in a partnership business. Sales Accounts Local Sales Income from sales within the country. Sales Accounts Export Sales Income from sales outside the country. Sales Accounts Sales of Services Income from services provided. Sales Accounts Sales of Goods Income from the sale of goods. Sales Accounts Sales Returns Returns of sold goods. Purchase Accounts Local Purchases Cost of goods purchased from local suppliers. Purchase Accounts Import Purchases Cost of goods purchased from foreign suppliers. Purchase Accounts Purchase of Raw Materials Cost of raw materials purchased for production. Purchase Accounts Purchase of Office Supplies Cost of office supplies purchased. Purchase Accounts Purchase Returns Returns of purchased goods. Purchase Accounts Freight Inwards Cost of transportation for purchased goods. Direct Incomes Commission Received Income from commissions earned on sales. Direct Incomes Service Income Income from services provided. Direct Incomes Royalty Income Income from royalties. Direct Incomes Interest on Loans Given Interest earned on loans provided by the business. Direct Incomes Dividend Received Dividends received from investments. Direct Expenses Freight Inwards Transportation costs for bringing goods into the business. Direct Expenses Raw Material Purchases Costs of raw materials used in production. Direct Expenses Power & Fuel Expenses for power and fuel used in production. Direct Expenses Wages Wages paid to labor directly involved in production. Direct Expenses Factory Rent Rent for factory premises. Indirect Incomes Interest Received Income from interest earned on deposits. Indirect Incomes Rental Income Income from renting out property or equipment. Indirect Incomes Miscellaneous Income Income from other sources not directly related to core business. Indirect Incomes Profit on Sale of Assets Gain from the sale of fixed assets. Indirect Incomes Discount Received Discounts received on purchases. Indirect Expenses Rent Expenses related to renting office space. Indirect Expenses Salary Payments made to employees. Indirect Expenses Office Expenses General office expenses (e.g., stationery, utilities). Indirect Expenses Telephone Expenses Costs of telephone and internet services. Indirect Expenses Travel Expenses Expenses for business travel. Indirect Expenses Advertising Expenses Costs related to marketing and advertising. Indirect Expenses Professional Fees Payments made to professionals (e.g., lawyers, accountants). Indirect Expenses Insurance Premium Costs of insurance for business assets. Indirect Expenses Repairs & Maintenance Costs of maintaining and repairing business assets. Indirect Expenses Bad Debts Amounts written off as unrecoverable debts. Branch/Divisions Branch A Tracks transactions specific to Branch A. Branch/Divisions Branch B Tracks transactions specific to Branch B. Branch/Divisions Division 1 Records transactions related to Division 1. Branch/Divisions Division 2 Records transactions related to Division 2. Miscellaneous Expenses Preliminary Expenses Expenses incurred during the formation of the company. Miscellaneous Expenses Deferred Revenue Expenditure Expenses to be written off gradually over time. Miscellaneous Expenses Promotional Expenses Expenses for promoting new products or services. Miscellaneous Expenses Legal Fees Legal costs that are amortized over time. Secured Loans Mortgage Loan Loans secured against property. Secured Loans Car Loan Loans secured against a vehicle. Secured Loans Equipment Loan Loans secured against business equipment. Secured Loans Term Loan Secured long-term loan. Unsecured Loans Personal Loan Loans taken without any collateral. Unsecured Loans Overdraft Bank overdraft facility. Unsecured Loans Loan from Friends Unsecured loans taken from friends. Unsecured Loans Loan from Relatives Unsecured loans taken from relatives. Suspense Account Suspense Temporary account for uncertain or incomplete transactions. Stock-in-Hand Finished Goods Value of goods that are ready for sale. Stock-in-Hand Raw Materials Value of raw materials held in inventory. Stock-in-Hand Work in Progress Value of unfinished goods in the production process. Stock-in-Hand Packing Materials Value of materials used for packing goods. Deposits (Asset) Security Deposit Deposits made for securing premises or equipment. Deposits (Asset) Fixed Deposit Money deposited in fixed-term accounts. Deposits (Asset) Rental Deposit Deposit paid for renting premises. Deposits (Asset) Telephone Deposit Deposit paid for telephone services.
