- Python Installation Step by Step
- Variables and Data Types (with Examples & Output)
- Python – Operators and Expressions
- Control Flow Statements in Python
- Data Structures in Python – Complete Notes
- Python Objects – Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
- File Handling in Python: Read, Write, and Manage Files
- Exception Handling in Python
- Functions in Python
- Modules in Python
- Library and Packages in Python -Introduction
- What is __init__.py in Python?
- 🧑🏫 What is Class and Object in Python? | Simple Explanation for Beginners
- What is __init__() in Python? | Constructor Made Simple
- What is self in Python? | Easy Explanation with Examples
- Encapsulation in Python | Easy OOP Explanation for Beginners
- Inheritance in Python | Learn How One Class Can Use Another
- Polymorphism in Python | One Name, Many Uses
- Method Overriding in Python | Easy Explanation with Examples
- Abstraction in Python | Hiding the Complex, Showing Only the Needed
- Difference Between Abstraction and Encapsulation in Python | Simple Words + Examples
- Most Used Libraries and Packages in Python | Easy Guide for Beginners
- How to Create Your Own Python Package (Step-by-Step Guide)
- Most Used Python Libraries (with Usage & Why Popular)
- Career-Based Python Library Guide
- NumPy Complete Reference Guide (with Real-Life Examples & Interview Q&A)
- Pandas Complete Guide (Simple English + Real-Life Examples)
- Matplotlib, Data Cleaning with Pandas, and Excel Integration using Pandas with examples and outputs.
Tag: python beginner
-
Learn Python Step by Step
-
Python Installation Step by Step
1) Click to Download for Windows Operation System https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.13.1/python-3.13.1-amd64.exe
2)Run the installer (e.g., python-3.x.x.exe).
3) On the first installation screen:
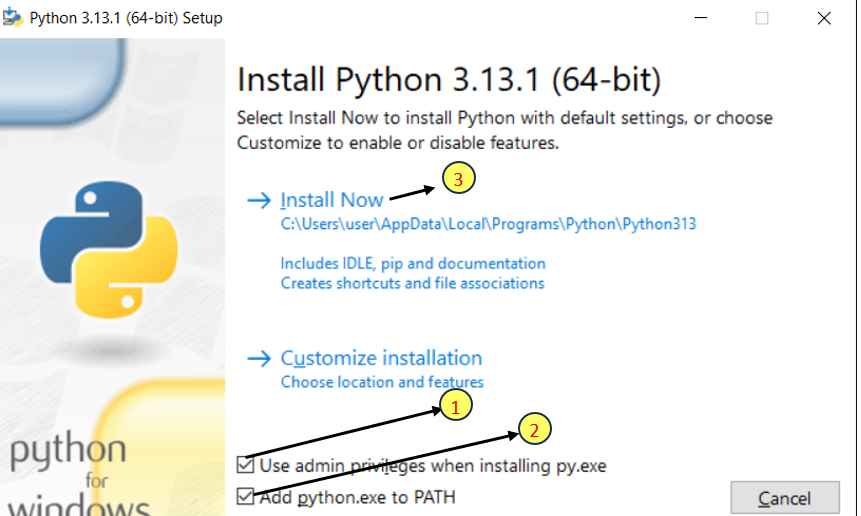
3.1) Check the box for “Use admin privileges when installing py.exe” at the bottom.
3.2) Check the box for “Add Python to PATH” at the bottom.
3.3) Click “Install Now” for default settings.
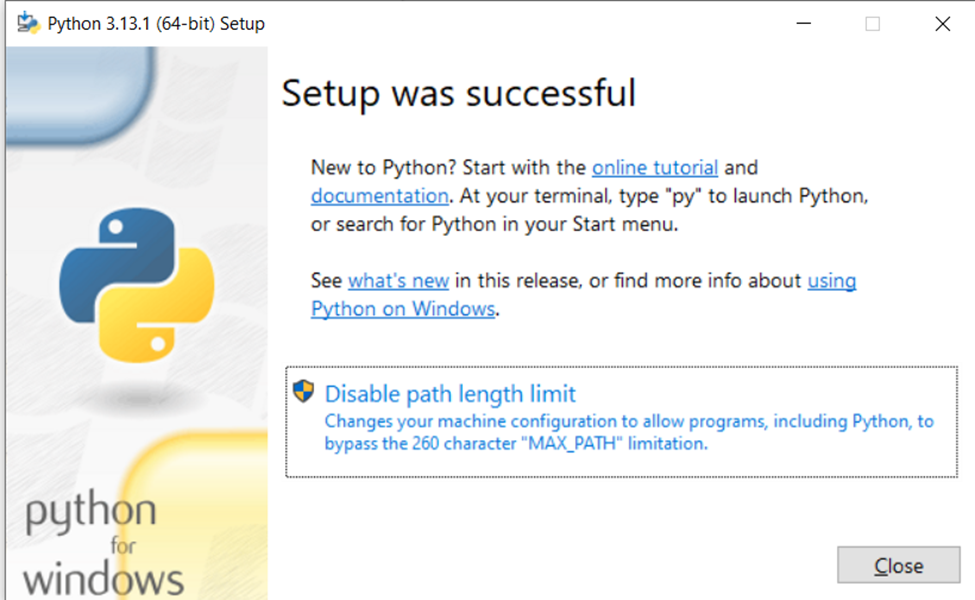
4) Wait for the installation to complete, and then click “Close”.
5)Open a Command Prompt.
5.1) In Search bar : Type CMD
5.2)Click Command Prompt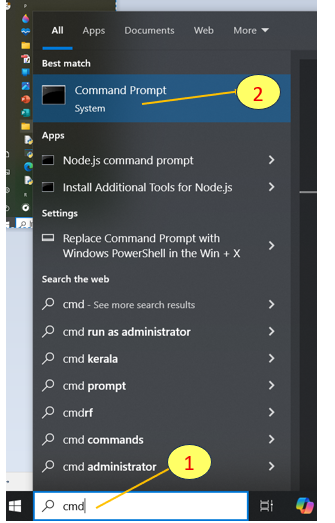
6) To Check If Python is Installed or Not
type python –version in Command Prompt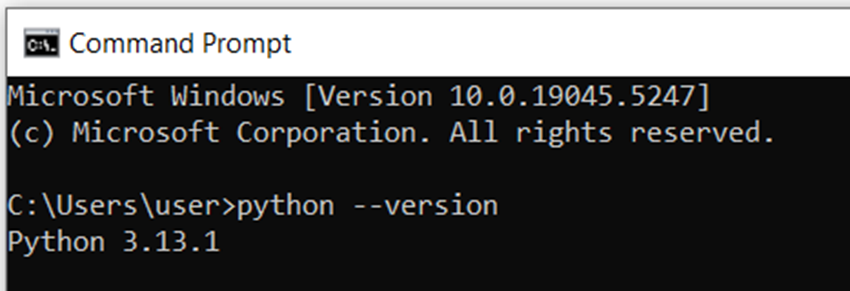
If a version number appears, Python is installed.
7) How to Use IDLE Window for to run Python Program
Interactive Mode
7.1) Type idle in Search bard
7.2) Click IDLE (python x.xx 64 bit)
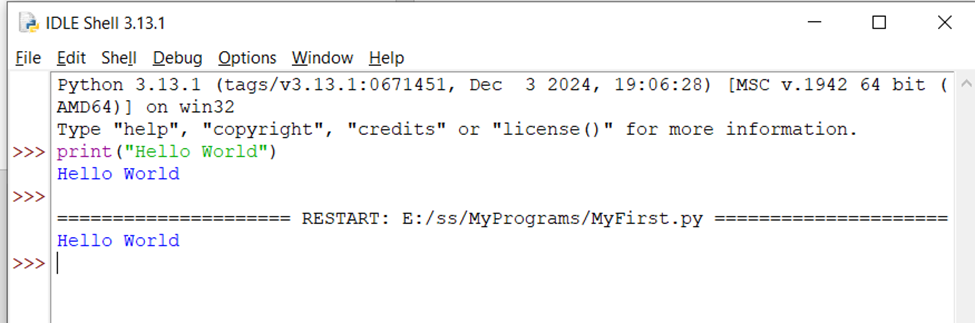
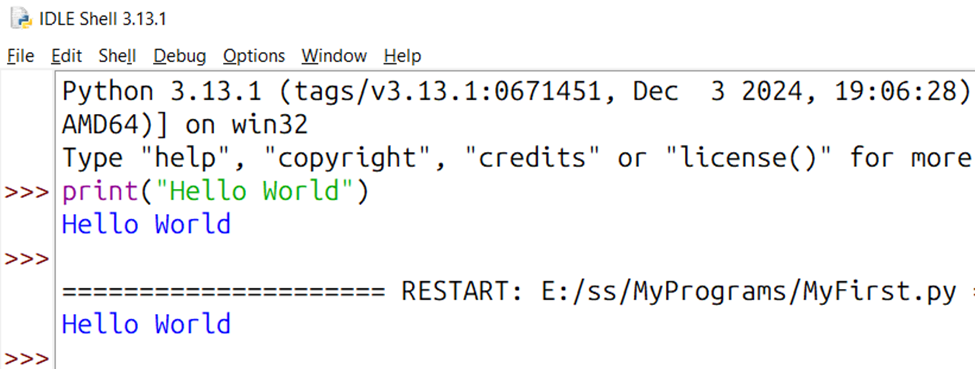
7.3) When IDLE opens, you’ll see the Python shell. You can type commands directly here, and they execute immediately.
type print(“Hello World”)
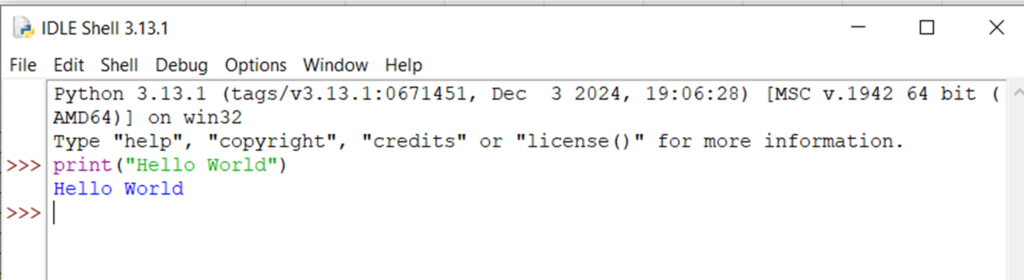
Press Enter to see the output.
Script Mode
To write and save Python programs:
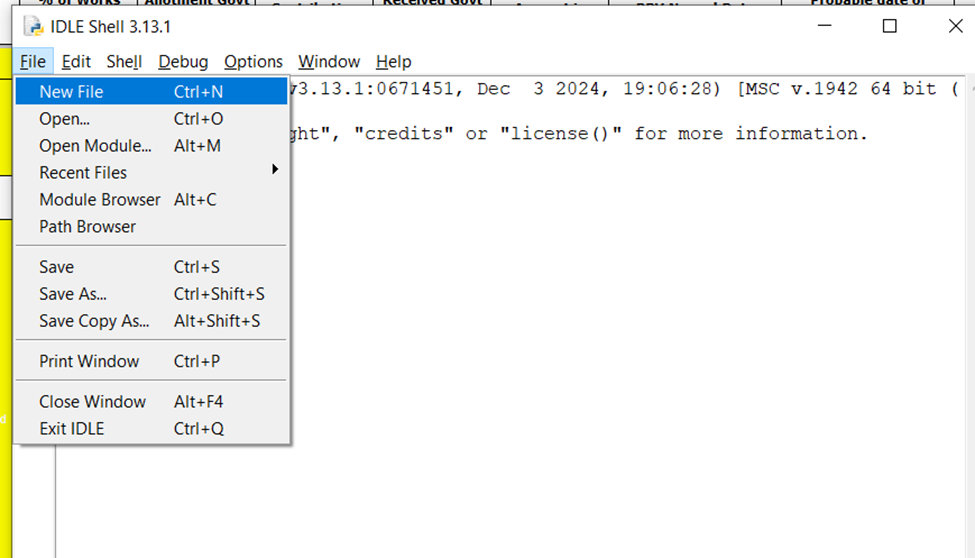
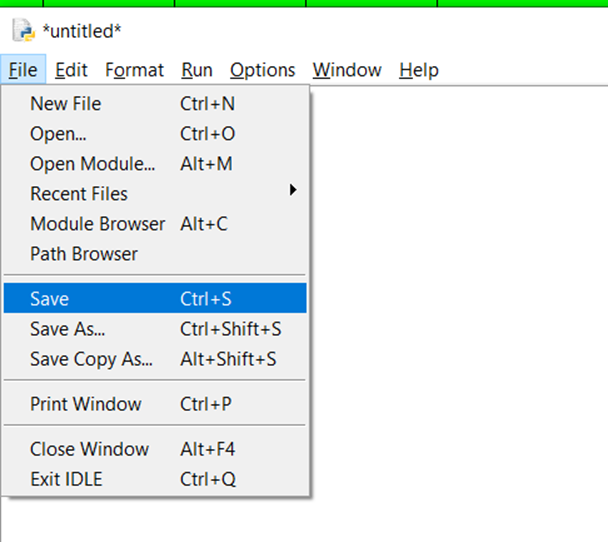
- Go to File → New File.
- A new editor window will open.
- Write your Python script here.
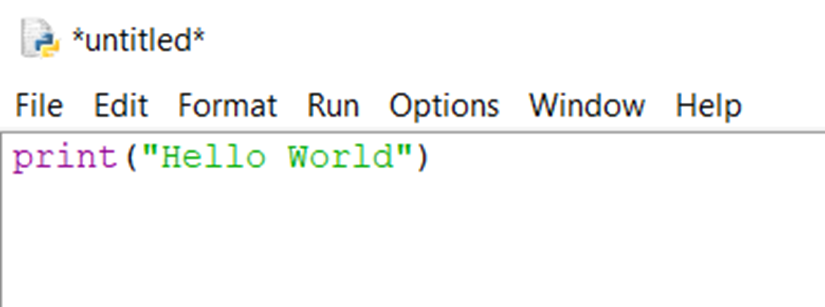
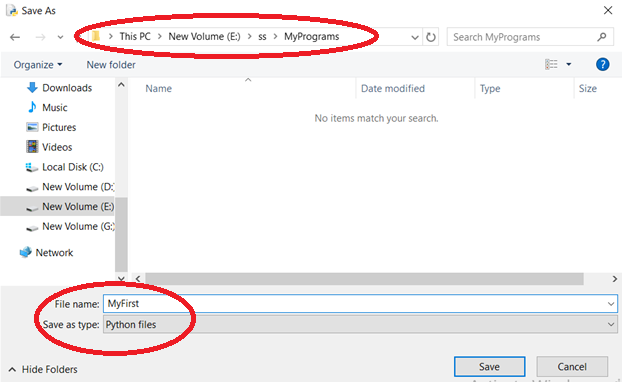
- Save the file (
Ctrl + S) with a.pyextension (e.g.,my_program.py).
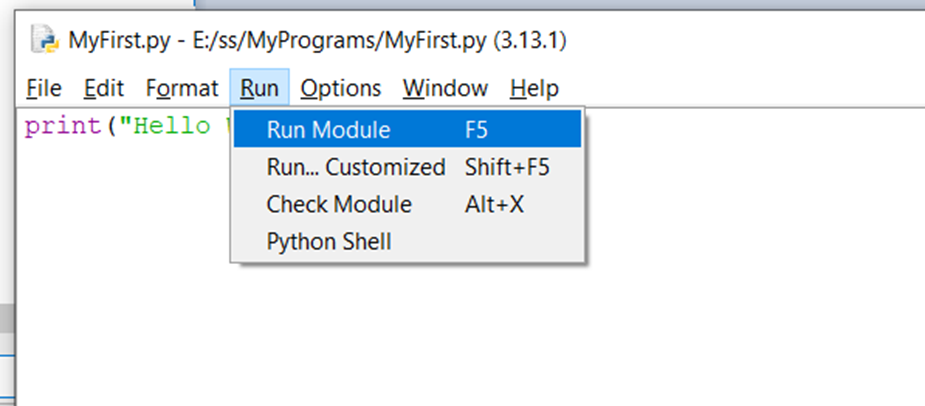
To run the script:
- Click Run → Run Module (
F5).
You Can Customize Settings: In IDLE, go to Options → Configure IDLE to adjust font size, colors, and other preferences.

-

Learn Python – Question and Answers
Table of Contents
Python Basics: Variables & Data Types – Q&A Session
1. What is a variable in Python?
- A. A storage container for data
- B. A type of loop
- C. A function for printing text
- D. A command to stop a program
2. Which of the following is a valid variable name in Python?
- A. 1name
- B. name_1
- C. name-1
- D. name!
3. What is the correct way to declare a string variable?
- A. name = “John”
- B. name = John
- C. “name” = John
- D. String name = “John”
4. In Python, which data type is used to represent decimal numbers?
- A. int
- B. str
- C. float
- D. bool
5. Which function is used to check the data type of a variable in Python?
- A. data()
- B. typeof()
- C. type()
- D. datatype()
6. What will be the output of the following code?
name = "Alice" print(type(name))- A. <class ‘str’>
- B. <class ‘int’>
- C. name
- D. Alice
7. Which of these is NOT a data type in Python?
- A. str
- B. int
- C. list
- D. decimal
8. What value will the following code output?
age = 30 age = "thirty" print(age)- A. 30
- B. “thirty”
- C. SyntaxError
- D. None
9. Which data type represents True and False values in Python?
- A. int
- B. str
- C. bool
- D. float
10. In Python, which symbol is used to assign a value to a variable?
- A. ==
- B. =
- C. :
- D. ->
Python Basics: Conditional Statements – Q&A Session
Question 1: Which statement is used to check a condition in Python?
- A. else
- B. elif
- C. if
- D. then
Question 2: What will the following code print if
x = 10?if x > 5: print("High") else: print("Low")- A. “High”
- B. “Low”
- C. “None”
- D. Error
Question 3: In Python, what does elif stand for?
- A. Else if
- B. Eliminate if
- C. Exit if
- D. Error
Question 4: Which operator checks if two conditions are both true?
- A. or
- B. and
- C. not
- D. ==
Question 5: What is the output of this code?
if 5 < 10 or 8 > 10: print("Yes")- A. No
- B. None
- C. Yes
- D. Error
Question 6: What is required in the if statement to compare values?
- A. =
- B. ==
- C. ===
- D. equals
Question 7: Which condition is met in this code?
if 20 > 25: print("A") elif 20 == 20: print("B") else: print("C")- A. A
- B. B
- C. C
- D. None
Question 8: How many possible conditions can elif handle?
- A. One
- B. Two
- C. Infinite
- D. None
Question 9: Which logical operator reverses a condition?
- A. or
- B. not
- C. and
- D. reverses
Question 10: What is a common mistake when using conditionals?
- A. Forgetting else
- B. Using == for assignment
- C. Using = instead of ==
- D. Indentation
Python Basics: Loops – Q&A Session
Question 1: Which loop runs as long as its condition is true?
- A. for
- B. while
- C. repeat
- D. loop
Question 2: What function generates a sequence of numbers in Python?
- A. sequence()
- B. list()
- C. range()
- D. num()
Question 3: What will
for i in range(3): print("Hi")print?- A. Hi three times
- B. Hi four times
- C. Hi two times
- D. None
Question 4: How can we stop a loop early?
- A. continue
- B. stop
- C. exit
- D. break
Question 5: What does the continue statement do in a loop?
- A. Skips the rest of the loop
- B. Skips to the next iteration
- C. Stops the loop
- D. Repeats the loop
Question 6: What is printed by
for i in range(5): if i == 3: break print(i)- A. 0, 1, 2
- B. 0, 1, 2, 3
- C. 0, 1
- D. None
Question 7: Which loop would you use to repeat code until a condition changes?
- A. for
- B. while
- C. until
- D. loop
Question 8: When is the else block in a loop executed?
- A. Always
- B. Only if break is used
- C. Only if continue is used
- D. When loop completes normally
Question 9: What is the result of
while False: print("Hello")?- A. Prints “Hello”
- B. Error
- C. No output
- D. Prints infinitely
Question 10: Which of these is not a loop in Python?
- A. for
- B. while
- C. loop
- D. Both B and C
Visit the Google Form Link:
Click on the link to access the quiz form. You will be redirected to a Google Forms page where you can start answering the questions.Answer the Questions:
Go through each question carefully and select or type your answers based on the options provided.Click ‘Submit’:
Once you’ve answered all the questions, scroll down and click the “Submit” button to submit your answers.View Your Score:
After submitting, click on the “View Score” button to see your results immediately. You will receive feedback on your performance.Variables & Data Types https://forms.gle/22qQ2UkhGKUvW4XE6 How to use Conditional Statements if ,elif, else https://forms.gle/7VjTGRVoYpNRKyLS8 For and While Loops– https://forms.gle/nj9f5eEE3yhA8sNs9 List Creation https://forms.gle/ccy1hmAx1fYH294B9 Dictionaries https://forms.gle/azRDkfEcPtQEhDqm6 Tuples https://forms.gle/7zuHYNJmVFnET6QZA -
Learn Python in Tamil | Python Basics | How to use Conditional Statements if ,elif, else
More Examples :
1. Basic if-else Statement:
number = 10 if number > 5: print("The number is greater than 5.") else: print("The number is 5 or less.")2. Multiple Conditions with
elif:marks = 85 if marks >= 90: print("Grade: A") elif marks >= 75: print("Grade: B") elif marks >= 50: print("Grade: C") else: print("Grade: F")3. Nested
ifStatements:age = 25 if age >= 18: if age >= 21: print("Eligible for a full license.") else: print("Eligible for a provisional license.") else: print("Not eligible for a license.")4. Using Logical Operators:
score = 85 attendance = 90 if score > 80 and attendance > 85: print("You passed with good standing!")5. Error Handling with Conditionals:
try: age = int(input("Enter your age: ")) if age >= 18: print("You are eligible to vote.") else: print("You are not eligible to vote.") except ValueError: print("Please enter a valid number.") -
Python – Functions Examples
Example 1 :
# Define a function def greet(): print("Hello, World!") # Call the function greet()Output :
Hello, World!Example 2 :
# Define a function with parameters def greet(name): print(f"Hello, {name}!") # Call the function with an argument greet("Alice")Output :
Hello, Alice!Example 3 :
# Define a function with two parameters def add(a, b): return a + b # Call the function with arguments result = add(3, 4) print(result)Output :
7Example 4 :
# Define a function that returns a value def square(x): return x * x # Call the function and store the result result = square(5) print(result)Output :
25Example 5 :
# Define a function that returns multiple values def get_name_and_age(): name = "Alice" age = 30 return name, age # Call the function and unpack the result name, age = get_name_and_age() print(name, age)Output :
Alice 30Example 6 : (Area of Circle using Functions)
def areaofcircle(r): answer=3.14*r return answer radius=int(input("Enter Radius Value")) ans=areaofcircle(radius) print ("Answer",ans)Output :
Enter Radius Value 1 Answer 3.14Example 7 :
def welcome(myname): msg="Hi " +myname + " Welcome to My Centre" return msg; m=input("Enter Your Name : ") print(welcome(m))Output :
Enter Your Name : Raj Hi Raj Welcome to My Centre
